Types of waste ponds and their functions
1. Cooling Pond
Cooling Pond Palm Oil Mill Effluent is a place or sludge storage pool to reduce the raw sludge temperature of the sludge pit, which is + 70 – 80oC to + 40 – 45oC to suit mesophilic bacteria.
- Function: The cooling pond is designed to reduce the temperature of raw sludge from the sludge pit. The sludge enters the cooling pond at a high temperature of about 70 – 80°C and is cooled down to approximately 40 – 45°C. This cooling process is essential to create suitable conditions for mesophilic bacteria.
- Explanation: Mesophilic bacteria, which are the main microbial agents involved in POME treatment, thrive at moderate temperatures. The cooling pond ensures that the sludge’s temperature is within the mesophilic range for effective biological treatment.
2. Mixing Pond
Mixing Pond Palm Oil Mill Effluent is a place or sludge storage pond after cooling from the cooling pond to neutralize the pH of the raw effluent by mixing the sludge from the anaerobic pond with a certain ratio. The ratio used is 1: 3, where for example, if the feeding from the cooling pond to the mixing pond is 200 tons / hour, then the back mix from anaerobic to the mixing pond is 600 tons / hour.
- Function: The mixing pond serves to neutralize the pH of the raw effluent by blending the sludge from the anaerobic pond with a specific ratio, typically 1:3. This neutralization is crucial to prepare the POME for subsequent treatment processes.
- Explanation: The pH of POME can be highly acidic, and adjusting it to a more neutral range is vital for the growth of beneficial microorganisms in later stages of treatment. Mixing helps distribute the anaerobically treated sludge into the effluent uniformly.
3. Anaerobic Pond
- Function: The anaerobic pond is primarily a storage facility for the anaerobic treatment of organic materials found in POME. It relies on mesophilic bacteria to break down organic matter in the wastewater.
- Explanation: Anaerobic treatment occurs without the presence of oxygen and is effective at removing organic pollutants. To facilitate this process, the anaerobic pond maintains specific conditions, such as a neutral pH, a temperature range of 30-40°C, the presence of necessary nutrients (nitrogen and phosphate), a certain pool depth, and a residence time of around two days.
Anaerobic Pond Palm Oil Mill Effluent is a storage pool for remodeling organic materials contained in wastewater using mesophilic bacteria. Where these bacteria can live with the following conditions:
1. Neutral pH, namely 6-9.
2. The temperature of the anaerobic pool is maintained between 30-40oC.
3. Adequate nutrition contains Nitrogen and Phosphate.
4. The pool depth is 5-6m.
5. Strive to make efforts to accommodate the waste for 2 days.
4. Contact Pond
Contact Pond Palm Oil Mill Effluent is a temporary storage pond for liquid waste from the anaerobic pond before being pumped into the land application.
- Function: The contact pond acts as a temporary holding area for liquid waste from the anaerobic pond before it is pumped for land application or further treatment.
- Explanation: After anaerobic treatment, the POME is often moved to the contact pond to await the next step in the treatment process. This can include further biological treatment or land application, depending on the mill’s specific practices.
5. Aerobic Pond
Aerobic pond is a liquid waste storage pool that aims to reduce organic materials by using aerobic bacteria.
- Function: The aerobic pond is designed to further reduce organic materials in POME by utilizing aerobic bacteria.
- Explanation: Aerobic bacteria require oxygen to metabolize organic matter. In this pond, organic pollutants are broken down in the presence of oxygen. This step helps to further treat and clarify the effluent, reducing its organic load before final discharge or disposal.

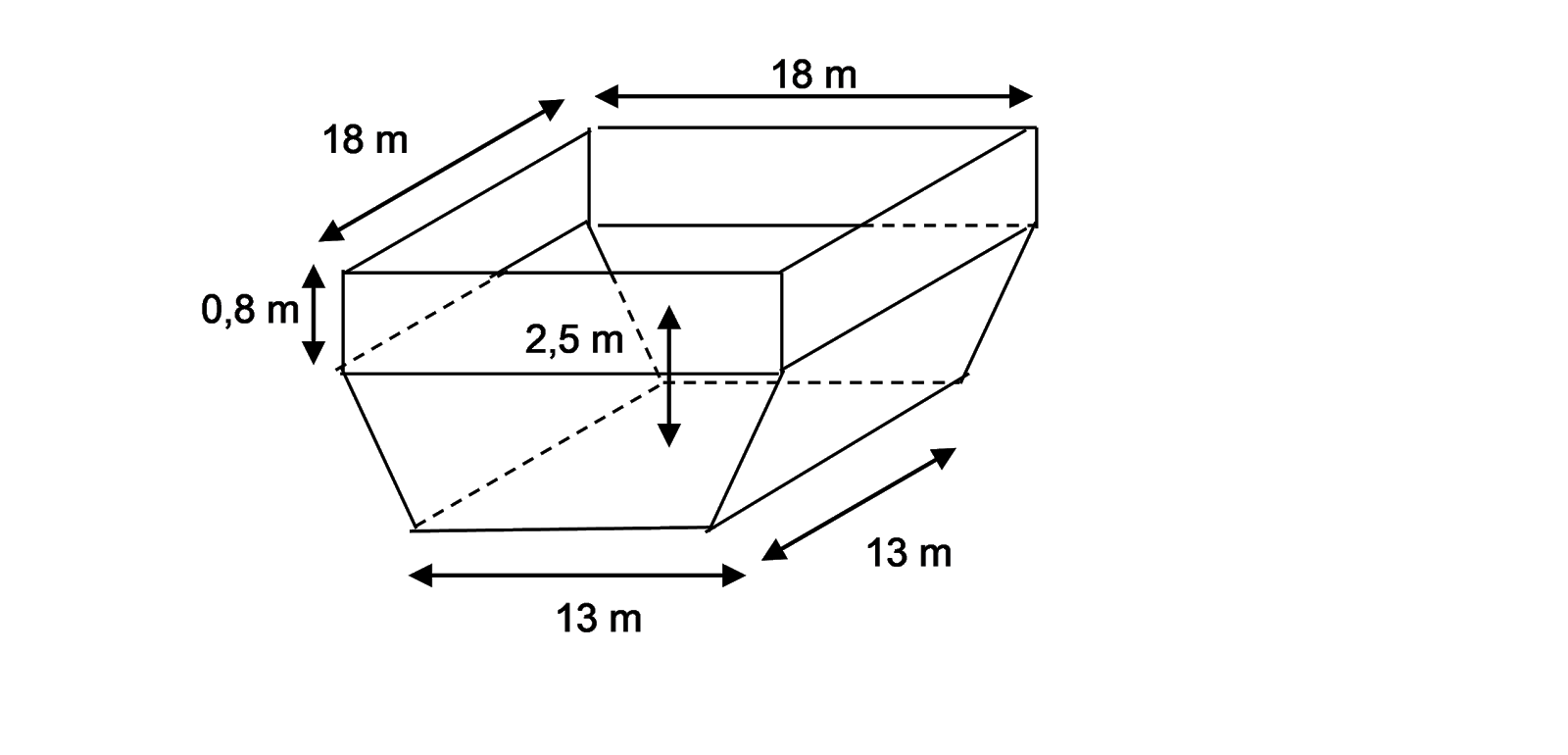





Pneumatic Tool For Rivet Nut