alwepo.com, Using Thread Rolling Machine – Thread rolling machine play a crucial role in manufacturing industries by efficiently producing high-quality threaded components. However, maximizing the performance of these machines requires knowledge of proper setup, operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting techniques.
In this comprehensive guide, we provide essential tips for utilizing thread rolling machines effectively, covering everything from setup to safety precautions.
Thread Rolling Machine Setup Guide
Thread rolling machine setup is a crucial process that directly impacts the quality and consistency of the threaded components produced. Proper setup ensures that the machine operates efficiently and effectively, minimizing errors and maximizing productivity. Below is a detailed explanation of each step involved in the thread rolling machine setup guide:
1. Choose the Right Machine
Selecting the appropriate thread rolling machine is the first step in the setup process. Considerations should include the size and type of threads required for production. Factors such as thread diameter, pitch, and thread form (internal or external) should be taken into account when choosing the machine.
Additionally, the capacity of the machine in terms of thread size and production volume should match the requirements of the intended application. It’s essential to ensure that the chosen machine is capable of accommodating the desired thread specifications to achieve the desired results.
2. Install Thread Rolling Dies
Once the appropriate machine is selected, the next step is to install the thread rolling dies. Thread rolling dies are precision tools that form the threads on the workpiece. It’s crucial to ensure that the dies are securely installed and aligned with the workpiece to prevent misalignment issues during operation.
Proper alignment of the dies helps maintain thread accuracy and prevents defects in the threaded components. Care should be taken to install the dies according to the manufacturer’s guidelines, ensuring that they are tightly secured and properly positioned relative to the workpiece.
3. Set Machine Parameters
After installing the dies, the machine parameters need to be adjusted to match the material and thread specifications. Machine settings such as feed rate, speed, and pressure play a critical role in determining the quality and efficiency of the thread rolling process. The feed rate controls the rate at which the workpiece is fed into the rolling dies, while the speed dictates the rotational speed of the dies. Pressure settings regulate the amount of force applied to the workpiece during the rolling process.
These parameters should be adjusted based on factors such as material hardness, thread size, and desired thread profile. It’s essential to consult the machine manual and refer to industry standards when setting these parameters to ensure optimal performance and thread quality.
4. Verify Alignment
Once the machine parameters are set, it’s important to verify the alignment of the workpiece and dies before initiating the rolling process. Misalignment between the workpiece and dies can result in thread defects such as off-center threads, incomplete threads, or thread laps. To verify alignment, visually inspect the positioning of the workpiece relative to the dies and make any necessary adjustments to ensure proper alignment.
Additionally, use precision measuring tools such as calipers or micrometers to confirm the alignment accuracy. Taking the time to verify alignment before starting production helps prevent costly errors and ensures consistent thread quality throughout the manufacturing process.
Operating a Thread Rolling Machine
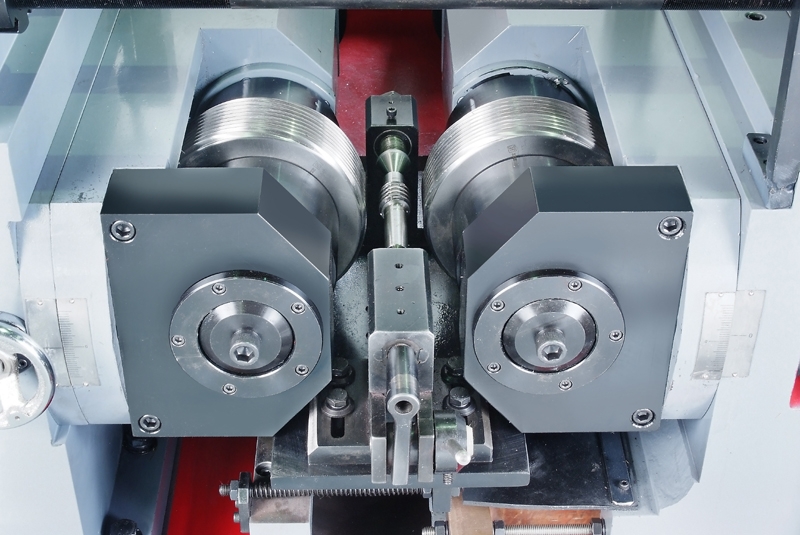
Operating a thread rolling machine efficiently and effectively requires attention to detail and adherence to best practices to ensure smooth operation and high-quality threaded components. Below is a detailed explanation of each aspect involved in operating a thread rolling machine:
1. Monitor Machine Performance
Keeping a close watch on machine performance is essential for identifying any potential issues or abnormalities that may affect the quality of threaded components. Machine indicators such as noise levels, vibration, and temperature can provide valuable insights into the condition of the machine. Unusual noises or excessive vibration may indicate mechanical problems, while abnormal temperature fluctuations could signal overheating or inadequate lubrication.
Regular monitoring of these indicators allows operators to detect problems early on and take corrective action to prevent production delays or quality issues.
2. Control Feed and Speed
Optimizing the feed rate and speed settings of the thread rolling machine is crucial for achieving the desired thread profile while minimizing wear on the dies. The feed rate controls the rate at which the workpiece is fed into the rolling dies, while the speed dictates the rotational speed of the dies. Adjusting these parameters based on factors such as material properties, thread size, and desired thread depth ensures optimal thread formation and extends the life of the dies.
Operators should refer to machine manuals and industry standards to determine the appropriate feed rate and speed settings for specific applications.
3. Maintain Proper Lubrication
Adequate lubrication is essential for reducing friction and preventing overheating during the thread rolling process. Proper lubrication ensures smooth material flow and prevents premature wear on the dies, resulting in longer tool life and improved thread quality.
Operators should regularly check and replenish lubricant levels to ensure consistent performance throughout the production run. The type of lubricant used may vary depending on the material being rolled and the operating conditions. It’s essential to use lubricants recommended by the machine manufacturer to avoid compatibility issues and ensure optimal performance.
4. Inspect Finished Threads
Regular inspection of the quality of the produced threads is critical for identifying any defects or inconsistencies that may arise during the rolling process. Inspecting finished threads allows operators to detect issues such as thread laps, tears, or incomplete threads early on and take corrective action to prevent scrap or rework.
Operators should use precision measuring tools such as thread gauges, calipers, or micrometers to verify thread dimensions and ensure compliance with specifications. By conducting regular inspections, operators can maintain consistent thread quality and minimize the risk of defects in the final product.
Best Practices for Thread Rolling
Thread rolling is a fast and efficient method for creating high-quality threads on cylindrical workpieces. However, to achieve optimal results, following best practices is crucial. Here’s a detailed breakdown of key practices to consider:
1. Selecting the Right Thread Rolling Dies
- Match the Thread Profile: The dies should have the exact profile of the thread you want to create (e.g., metric, imperial, etc.). Mismatched profiles will result in incorrect or defective threads.
- Consider Thread Size: Ensure the die size corresponds to the diameter of the threads you need. Using oversized dies can lead to weak threads, while undersized ones won’t form the threads properly.
- Material Compatibility: Choose dies made from a material suitable for the workpiece material being rolled. For example, high-strength steel dies are needed for tough materials.
2. Optimizing Thread Rolling Speed and Feed
- Material Properties: Softer materials can handle higher speeds and feeds, while harder materials require slower speeds and lower feeds to avoid excessive strain or tool damage.
- Thread Size: Larger threads generally require slower speeds and feeds compared to smaller threads.
- Desired Thread Depth: Deeper threads might necessitate slower speeds to allow for proper material flow and complete thread formation.
3. Lubricating for Thread Rolling
- Friction Reduction: A proper lubricant minimizes friction between the dies and the workpiece. This reduces wear on the dies, lowers rolling force requirements, and improves surface finish.
- Die Life Extension: Lubrication protects the dies from excessive wear and tear, extending their lifespan.
- Surface Finish Enhancement: The right lubricant helps create a smoother and more polished surface finish on the rolled threads.
4. Achieving Good Surface Finish
- Die Condition: Regularly inspect the thread rolling dies for wear and damage. Worn or chipped dies will produce rough or uneven surface finishes. Replace dull or damaged dies promptly.
- Die Alignment: Ensure proper alignment of the dies to guarantee consistent pressure distribution and a uniform surface finish across the entire thread.
5. Minimizing Thread Rolling Defects
- Proper Setup: Following the manufacturer’s instructions for setting up the thread rolling machine is crucial. Incorrect setup can lead to a variety of defects.
- Machine Cleanliness: Maintaining a clean machine helps prevent contamination and foreign particles from getting embedded in the threads, which can cause imperfections.
- Thread Inspection: Regularly inspect the rolled threads for defects like thread laps (incomplete formation) or tears (material breakage). Identifying and addressing these issues early helps maintain quality control.
Thread Rolling Machine Troubleshooting
Even with meticulous setup and operation, thread rolling machines can encounter problems. Here’s a breakdown of common issues and how to tackle them:
1. Misalignment Blues
- Symptoms: Uneven or poorly formed threads, thread laps (incomplete thread formation on one side), or binding during the rolling process.
- Solution: Stop the machine and check the alignment between the workpiece and the dies. Most machines have adjustment mechanisms to ensure the dies are perfectly centered relative to the workpiece. Meticulously realign the dies as per the manufacturer’s instructions.
2. Die Wear and Tear
- Symptoms: Rough or damaged threads, threads with incorrect dimensions (undersized or oversized), or increased rolling force required.
- Solution: Regularly inspect your thread rolling dies for wear and tear. Look for signs of chipping, dulling, or excessive wear on the thread profile. If the dies are damaged or worn beyond a certain point, replace them with new ones to maintain thread quality and dimensional accuracy.
3. Feed and Speed Shenanigans
- Symptoms: Stripped threads (material tearing away), incomplete threads, or excessive burrs on the threads.
- Solution: Analyze the issue and adjust the feed and speed settings accordingly. Here’s a guideline:
- Thread Stripping: Reduce the feed rate or increase the speed to allow more material flow and prevent excessive pressure on the threads.
- Incomplete Threads: Increase the feed rate or reduce the speed to allow for more material deformation and complete thread formation.
- Excessive Burrs: Reduce the feed rate slightly.
Remember: Refer to your machine’s manual and die supplier’s recommendations for specific feed and speed adjustments based on your material properties, thread size, and desired thread depth.
Thread Rolling Machine Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for prolonging the life of thread rolling machines and ensuring consistent performance. Follow these maintenance tips:
1. Cleanliness is Key
- Regularly clean the machine to remove debris, metal chips, and lubricant buildup. Contamination can hinder performance and lead to machine wear.
- Pay particular attention to areas around the dies and the workpiece placement area.
- Use appropriate cleaning methods following the manufacturer’s recommendations. This might involve compressed air, brushes, and cleaning solvents suitable for the machine’s components.
2. Die Inspection: A Keen Eye for Quality
- Inspect your thread rolling dies regularly for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Worn or damaged dies can produce poor-quality threads with dimensional inaccuracies.
- Look for chipping, cracks, or dulling on the thread profile. Misalignment can cause uneven or incomplete thread formation.
- Address any issues promptly. Replace worn or damaged dies and realign them if necessary to maintain thread quality and accuracy.
3. Lubrication: The Oil of Efficiency
- Ensure all moving parts of the machine are adequately lubricated according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Proper lubrication reduces friction, minimizes wear on machine components, and extends the machine’s lifespan.
- Use the recommended lubricant type and viscosity for your machine. Apply lubricant at designated intervals, following the manufacturer’s lubrication chart.
4. Calibration: Ensuring Precision
- Periodically calibrate your thread rolling machine to maintain accuracy and consistency in thread production. Calibration involves checking and adjusting various machine settings to ensure they meet the desired specifications.
- The frequency of calibration depends on factors like usage, material type, and required thread tolerances. Consult the manufacturer’s recommendations for calibration intervals specific to your machine.
Additional Maintenance Tips:
- Machine Manual: Refer to your machine’s manual for specific maintenance procedures and recommended maintenance schedules.
- Training: Ensure your machine operators are properly trained on maintenance procedures to guarantee they are performed correctly and consistently.
- Record Keeping: Keep a maintenance log to document all maintenance activities performed on the machine, including the date, type of maintenance, and any parts replaced. This helps track maintenance trends and identify potential issues early on.
Thread Rolling Machine Safety Precautions
Thread rolling machines, while efficient, require prioritizing safety to prevent accidents and injuries. Here’s a breakdown of essential safety precautions to follow:
1. Gear Up with Proper PPE
- Eyes: Wear safety glasses or a face shield to protect your eyes from flying debris or metal chips that could be ejected during the rolling process.
- Hands: Use appropriate gloves to provide protection from cuts, abrasions, and pinches that might occur while handling workpieces or adjusting the machine.
- Hearing: Consider wearing hearing protection if your thread rolling machine operates at high noise levels to safeguard your hearing.
2. Follow the Machine’s Lead
- Manufacturer’s Manual: Treat your machine’s manual as your safety bible. Read and understand the manufacturer’s instructions thoroughly before operating the machine.
- Safety Guidelines: Pay close attention to the specific safety guidelines outlined in the manual. These guidelines will address proper operating procedures, potential hazards, and emergency shutdown procedures.
- Training: If operator training is offered by the manufacturer, ensure all personnel operating the machine undergo proper training to be familiar with its safe operation.
3. Keep Your Distance
- Moving Parts: Maintain a safe distance from all moving parts of the machine, especially the rotating dies. Loose clothing or jewelry can get caught in moving parts, leading to serious injuries.
- Die Area: Avoid placing your hands or fingers near the die area while the machine is operating. A single wrong move can result in serious crushing or cutting injuries.
4. Secure the Load
- Workpiece Clamping: Always ensure that the workpieces you are rolling are securely clamped or held in place using the designated fixtures. This prevents them from becoming projectiles if they get dislodged during the rolling process.
- Visual Inspection: Before starting the machine, visually inspect the workpiece placement and confirm it’s secure.
Additional Safety Tips:
- Never operate the machine if you are fatigued, under the influence of drugs or alcohol, or not feeling well.
- Report any malfunctions or safety hazards to a supervisor immediately.
- Maintain a clean and organized work area around the thread rolling machine to prevent tripping hazards or clutter that could hinder safe operation.
Conclusion
Mastering the use of thread rolling machines requires a combination of proper setup, operation, maintenance, and safety practices. By following the tips outlined in this guide, manufacturers can optimize thread rolling processes, achieve consistent thread quality, and enhance productivity. Whether selecting the right dies, optimizing machine settings, or ensuring safety in operation, attention to detail and adherence to best practices are key to success in thread rolling operations.
By implementing these tips, manufacturers can unlock the full potential of thread rolling machines and produce high-quality threaded components efficiently and reliably.













Leave a Reply
View Comments