alwepo.com, Pick and Place Robot – In the fast-paced world of industrial automation, pick and place robots have emerged as indispensable tools for enhancing productivity and streamlining manufacturing processes. These robotic systems are designed to automate repetitive tasks, ensuring consistency and precision in various industries.

This article will delve into the components of pick and place robots, explore their real-world applications, discuss the benefits and disadvantages of using these robots, and provide insights on how to choose the right robot for your business.
What Is Pick and Place Robots?
A pick and place robot is a type of industrial robotic system designed to automate the process of picking up objects from one location and placing them in another. These robots are commonly used in manufacturing and assembly processes to handle repetitive tasks with precision and efficiency. The primary function of a pick and place robot is to grasp objects using an end-effector, such as a gripper or suction cup, and transport them to a designated location for further processing or assembly.
Pick and place robots consist of several key components, including a mechanical arm (manipulator), end-effector, sensors, and a control system. The mechanical arm is responsible for executing pick and place operations, mimicking the movement capabilities of the human arm. The end-effector is the tool attached to the robot arm, enabling it to securely grasp objects. Sensors provide real-time feedback to the robot, allowing it to identify objects and adjust its movements accordingly. The control system, typically a programmable logic controller (PLC), governs the entire robot system and coordinates its operation.
These robots find extensive applications across various industries, including manufacturing, packaging, warehousing, food and beverage, and electronics. In manufacturing, pick and place robots are used for assembling components, placing parts on conveyor belts, and handling materials during production. In warehousing and logistics, they expedite order fulfillment by picking and placing items into boxes or containers with high accuracy. In the food industry, pick and place robots handle delicate and perishable items, ensuring product integrity and adhering to hygiene standards. In electronics manufacturing, these robots contribute to the precision and speed required for assembling electronic products.
The utilization of pick and place robots offers several benefits for businesses, including increased efficiency, precision, and cost savings. These robots operate at high speeds, boosting production rates and overall efficiency in manufacturing processes. They offer unparalleled precision in picking and placing objects, minimizing errors and ensuring consistency in assembly tasks. By automating repetitive tasks, companies can reduce labor costs and minimize human-related errors, leading to long-term cost savings and improved profitability.
Components of Pick and Place Robots
Pick and place robots are sophisticated industrial machines designed to automate the process of picking up objects from one location and placing them in another. These robots consist of several key components, each playing a crucial role in their operation. Understanding these components is essential for unlocking the full potential of pick and place robots. Let’s explore each component in detail:
1. Mechanical Arm (Manipulator)
- The mechanical arm, also known as the manipulator, serves as the primary component responsible for executing pick and place operations. It mimics the movement capabilities of the human arm, allowing the robot to reach, grasp, and manipulate objects with precision.
- The mechanical arm typically consists of joints and links that provide flexibility and maneuverability. These joints allow the arm to move along multiple axes, enabling complex motions required for picking up objects from various orientations and placing them accurately at the desired location.
- The design of the mechanical arm varies depending on the specific application requirements, such as reach, payload capacity, and workspace constraints. Some pick and place robots feature articulated arms with multiple degrees of freedom, while others may have simpler linear or gantry-style configurations.
2. End-Effector (Gripper)
- The end-effector, also referred to as the gripper, is the tool attached to the end of the mechanical arm, enabling the robot to grasp and hold objects securely during pick and place operations.
- Grippers come in various types and configurations to suit different applications and object geometries. Common types of grippers include:
- Mechanical Grippers: These grippers feature mechanical claws or fingers that close around the object to grip it securely.
- Suction Cups: Suction cup grippers use vacuum suction to hold objects with smooth, flat surfaces.
- Magnetic Grippers: Magnetic grippers are used for picking up ferrous objects by creating a magnetic attraction.
- The selection of the appropriate end-effector depends on factors such as the size, shape, weight, and material of the objects being handled, as well as the required grip strength and precision.
3. Sensors
- Sensors play a crucial role in enabling pick and place robots to perceive and interact with their environment. These sensors provide real-time feedback on object detection, position tracking, and environmental conditions, allowing the robot to adapt its movements accordingly.
- Common types of sensors used in pick and place robots include:
- Vision Systems: Cameras and image processing algorithms are used for object recognition, localization, and quality inspection.
- Proximity Sensors: These sensors detect the presence or absence of objects in the robot’s workspace, enabling collision avoidance and object detection.
- Force/Torque Sensors: Force and torque sensors measure the forces exerted on the gripper during object manipulation, allowing the robot to adjust its grip force and ensure safe handling.
- Sensor data is integrated into the robot’s control system to facilitate autonomous operation, feedback control, and error detection, ensuring accurate and efficient pick and place operations.
4. Control System
- The control system serves as the brain of the pick and place robot, governing its operation and coordination with other components. It comprises hardware and software components responsible for planning, executing, and monitoring pick and place tasks.
- The control system may include:
- Programmable Logic Controller (PLC): PLCs are commonly used for real-time control of industrial automation systems, including pick and place robots. They execute pre-programmed sequences of operations and coordinate the interactions between the robot, sensors, and peripheral devices.
- Motion Control System: Motion controllers regulate the movement of the robot’s mechanical arm, ensuring precise positioning and trajectory tracking.
- Human-Machine Interface (HMI): HMIs provide operators with a user-friendly interface for monitoring and controlling the robot’s operation, accessing diagnostic information, and configuring system parameters.
- The control system orchestrates pick and place tasks, interprets sensor data, and implements algorithms for motion planning, object recognition, and collision avoidance, enabling the robot to perform its tasks autonomously and efficiently.
Real-World Applications Pick and Place Robots
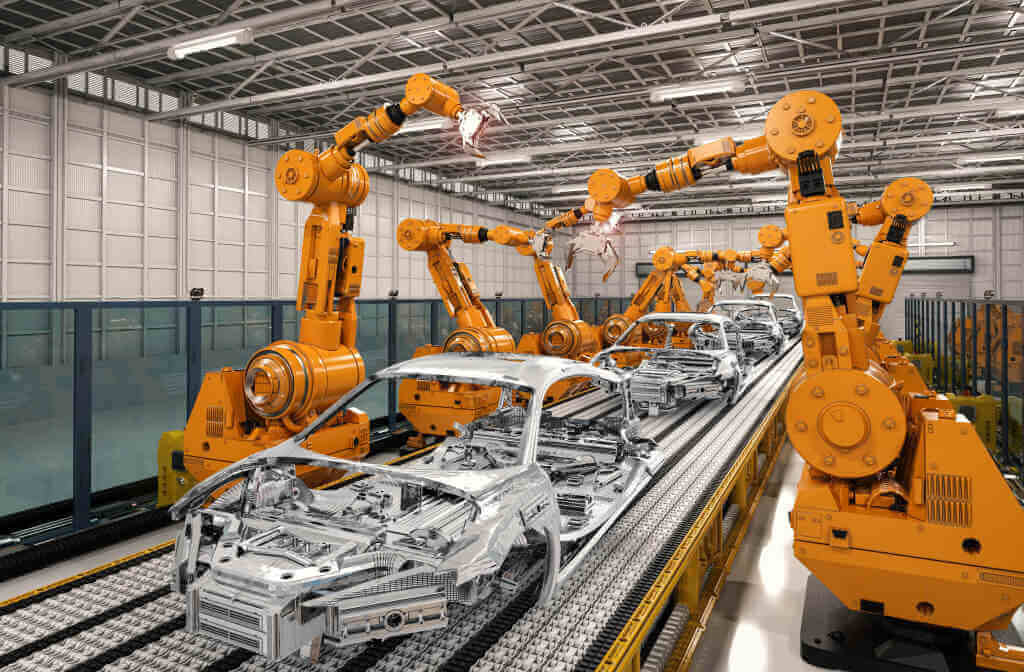

Pick and place robots have found extensive applications across a wide range of industries due to their versatility, precision, and efficiency in handling repetitive tasks. Here are some real-world applications of pick and place robots:
1. Manufacturing Industry
- Assembly: Pick and place robots are extensively used in the manufacturing industry for assembling products such as electronic devices, automotive components, consumer goods, and appliances. These robots can efficiently pick up individual parts and place them in precise positions for assembly, ensuring consistent product quality and high throughput.
- Material Handling: Pick and place robots excel in material handling tasks such as sorting, palletizing, and packaging. They can pick up items of various shapes, sizes, and weights from conveyor belts or storage bins and place them onto pallets, trays, or containers with speed and accuracy, streamlining warehouse operations and optimizing logistics processes.
2. Packaging and Warehousing
- Order Fulfillment: In e-commerce fulfillment centers and distribution warehouses, pick and place robots play a crucial role in picking, sorting, and packing orders for shipment. These robots can rapidly pick items from storage shelves or bins and place them into shipping containers or parcels, facilitating fast and accurate order processing.
- Palletizing and Depalletizing: Pick and place robots are also used for palletizing and depalletizing operations, where they stack or destack boxes, cartons, or bags onto or from pallets. By automating these tasks, companies can increase throughput, reduce labor costs, and improve workplace safety.
3. Food and Beverage Industry
- Packaging and Processing: Pick and place robots are widely employed in the food and beverage industry for packaging, processing, and handling food products. These robots can pick up items such as bottles, cans, pouches, and trays and place them into packaging containers, such as boxes, crates, or trays, ensuring hygienic handling and minimizing product damage.
- Sorting and Inspection: Pick and place robots equipped with vision systems are used for sorting and inspecting food products based on criteria such as size, shape, color, and quality. These robots can remove defective or contaminated items from the production line, ensuring compliance with food safety standards and minimizing waste.
4. Electronics Manufacturing
- Surface Mount Technology (SMT) Assembly: Pick and place robots are indispensable in electronics manufacturing for assembling printed circuit boards (PCBs) using surface mount technology (SMT). These robots can accurately pick up tiny electronic components, such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits, and place them onto PCBs with micron-level precision, ensuring reliable soldering and electrical connections.
- Testing and Inspection: Pick and place robots are also used for testing and inspecting electronic devices and components. These robots can transport devices to testing stations or inspection cameras, facilitating quality control checks and defect detection before final assembly or shipment.
5. Pharmaceutical and Medical Industry
- Drug Packaging: Pick and place robots are employed in pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities for packaging drugs, tablets, capsules, and other medical products into blister packs, bottles, or cartons. These robots can handle fragile or sensitive items with care, ensuring accurate counting and packaging.
- Lab Automation: In laboratories and medical research facilities, pick and place robots are used for automating sample handling, pipetting, and plate manipulation tasks. These robots can precisely transfer samples, reagents, and assay plates between instruments and workstations, increasing throughput and reducing manual errors.
Benefits of a Pick and Place Robot
Pick and place robots offer a plethora of benefits to businesses across various industries, making them indispensable tools for automating repetitive tasks and improving operational efficiency. Here, we delve into the detailed explanations of the key advantages of using pick and place robots:
1. Increased Productivity and Throughput
- One of the primary benefits of pick and place robots is their ability to significantly increase productivity and throughput in manufacturing and assembly processes. These robots can perform repetitive tasks with consistent speed and precision, resulting in faster cycle times and higher output rates.
- By automating manual handling and assembly tasks, pick and place robots eliminate bottlenecks and idle time in production, allowing businesses to meet increased demand and achieve higher production volumes without compromising quality.
2. Precision and Accuracy
- Pick and place robots offer unparalleled precision and accuracy in handling objects, ensuring that parts are positioned and placed with consistent repeatability. This precision is crucial in industries such as electronics manufacturing, where components must be placed on circuit boards with micron-level accuracy.
- Advanced sensors and vision systems enable pick and place robots to detect and adapt to changes in object position, orientation, and surface characteristics, further enhancing their accuracy and reliability in performing pick and place tasks.
3. Cost Savings and Efficiency
- Implementing pick and place robots can lead to significant cost savings for businesses by reducing labor costs, minimizing material waste, and optimizing resource utilization. By automating repetitive tasks, companies can reallocate human labor to more skilled or value-added activities, maximizing workforce productivity and efficiency.
- Pick and place robots also help minimize the risk of human-related errors, such as dropped or misplaced parts, which can result in costly rework, scrap, and product defects. By improving process consistency and reducing error rates, these robots contribute to overall cost reduction and improved profitability.
4. Versatility and Adaptability
- Pick and place robots are highly versatile and adaptable to a wide range of applications and industries. They can be programmed and reprogrammed to handle different types of objects, sizes, shapes, and materials, making them suitable for diverse manufacturing, assembly, and logistics tasks.
- With the ability to accommodate various end-effectors, such as grippers, suction cups, or specialized tools, pick and place robots can handle a wide range of objects with different handling requirements, from fragile electronic components to heavy industrial parts.
5. Improved Workplace Safety
- By automating repetitive and physically demanding tasks, pick and place robots help improve workplace safety by reducing the risk of injuries associated with manual handling, lifting, and repetitive motion. These robots can handle heavy or awkward objects with ease, eliminating the need for human operators to perform strenuous tasks.
- Additionally, pick and place robots are equipped with built-in safety features, such as collision detection sensors, emergency stop buttons, and safety interlocks, to prevent accidents and ensure safe operation in shared workspaces with human workers.
6. Flexibility and Scalability
- Pick and place robots offer flexibility and scalability to adapt to changing production demands and evolving business requirements. These robots can easily be reconfigured or reprogrammed to accommodate new product designs, process changes, or production volumes, providing businesses with agility and responsiveness in dynamic manufacturing environments.
- With modular designs and customizable configurations, pick and place robots can be integrated seamlessly into existing production lines or deployed as standalone systems, allowing businesses to scale automation capabilities according to their specific needs and growth objectives.
Disadvantages of Using A Robot
While pick and place robots offer numerous advantages, there are also several disadvantages and challenges associated with their use. It’s important for businesses to consider these factors when evaluating the implementation of robotic automation. Here are detailed explanations of the key disadvantages of using pick and place robots:
1. High Initial Investment
- One of the primary drawbacks of using pick and place robots is the high initial investment required for purchasing, installing, and integrating these systems into existing production processes. The cost of acquiring robotic equipment, including the robot itself, end-effectors, peripheral devices, and safety features, can be substantial, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with limited capital budgets.
- Additionally, the implementation of robotic automation may necessitate infrastructure upgrades, such as modifications to the production layout, installation of safety fencing or guarding, and integration with existing machinery and control systems, further increasing the upfront investment and complexity of deployment.
2. Complex Programming
- Programming pick and place robots can be complex and technically challenging, requiring specialized knowledge and expertise in robotics, automation, and programming languages. The process typically involves writing and debugging code to define motion trajectories, coordinate system transformations, and implement logic for object detection, localization, and manipulation.
- Skilled technicians or engineers with robotics training are often required to develop custom programs tailored to specific pick and place tasks and application requirements. This reliance on specialized programming expertise can pose challenges for businesses with limited in-house resources or expertise in robotics and automation.
3. Limited Adaptability
- While pick and place robots are versatile and flexible to a certain extent, they may face limitations in handling irregularly shaped, fragile, or variable objects, particularly in applications with diverse product mixes or fluctuating production volumes. Certain objects may be challenging for robots to grip or manipulate accurately, requiring additional customization or manual intervention.
- The design and programming of pick and place robots are optimized for specific tasks and environments, which may limit their adaptability to new or unforeseen challenges. Changes in product designs, materials, or production processes may necessitate reprogramming or reconfiguration of the robotic system, adding complexity and time to implementation.
4. Maintenance and Downtime
- Pick and place robots require regular maintenance and servicing to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and longevity. Mechanical wear and tear, component failures, and software glitches can occur over time, necessitating preventive maintenance, repairs, and component replacements.
- Downtime associated with maintenance activities, troubleshooting, and repairs can disrupt production schedules and reduce overall equipment effectiveness (OEE), impacting productivity and throughput. Businesses must allocate resources for spare parts inventory, technical support, and training to minimize downtime and maximize uptime.
5. Integration Challenges
- Integrating pick and place robots into existing production lines or workflows can pose integration challenges, particularly in legacy or heterogeneous environments with diverse equipment and control systems. Ensuring seamless communication and coordination between the robot and other machinery, sensors, and software systems may require custom interfaces, protocols, and middleware.
- Compatibility issues, interoperability constraints, and synchronization challenges may arise when integrating robotic automation with legacy equipment or proprietary technologies, requiring careful planning, testing, and validation to achieve smooth integration and interoperability.
6. Risk of Job Displacement
- The widespread adoption of pick and place robots and other forms of automation raises concerns about the potential impact on employment and job displacement. While robots can augment human labor by automating repetitive or hazardous tasks, they may also lead to the displacement of manual workers whose jobs are replaced by automated systems.
- Businesses must consider the social and ethical implications of automation and take proactive measures to mitigate the negative consequences of job displacement, such as investing in workforce training and reskilling programs, promoting human-robot collaboration, and fostering a culture of lifelong learning and adaptation.
Choosing the Right Robot

Choosing the right robot for a particular application or business requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure optimal performance, efficiency, and return on investment. Here’s a detailed explanation of the key considerations when selecting the right robot:
1. Task Analysis
- Conducting a thorough analysis of the automation task is the first step in choosing the right robot. This involves understanding the specific requirements of the application, including the type of tasks to be performed, the size and weight of objects to be handled, the speed and precision needed, and any environmental or safety considerations.
- By analyzing these factors, businesses can determine the appropriate robot specifications, such as reach, payload capacity, speed, and repeatability, to ensure that the selected robot can effectively meet the demands of the application.
2. End-Effector Selection
- Selecting the right end-effector, or tooling, is critical for the success of the automation system. The end-effector is the device attached to the robot arm that interacts with the objects being handled. Different end-effectors, such as grippers, vacuum suction cups, or specialized tools, are designed for specific applications and object types.
- Businesses should consider factors such as the size, shape, weight, and surface characteristics of the objects to be handled when choosing the appropriate end-effector. Additionally, specialized end-effectors may be required for tasks such as picking up delicate or irregularly shaped objects, applying adhesive or fasteners, or performing assembly operations.
3. Robot Specifications
Evaluating the specifications of available robots is essential to ensure compatibility with the application requirements. Key specifications to consider include:
- Reach: The maximum distance the robot arm can reach.
- Payload Capacity: The maximum weight the robot can lift or carry.
- Speed: The velocity at which the robot can move.
- Repeatability: The ability of the robot to return to a specific position with consistent accuracy.
- Degrees of Freedom: The number of axes or joints the robot arm can articulate, which affects its flexibility and maneuverability.
- Choosing a robot with the right specifications ensures that it can perform the required tasks efficiently and effectively without exceeding its capabilities.
4. Programming Ease and Compatibility
- Consider the ease of programming and compatibility of the robot with existing systems and software. User-friendly programming interfaces and software tools can streamline the setup and operation of the robot, reducing programming time and training requirements.
- Compatibility with common programming languages, such as C++, Python, or graphical programming environments, may also be important for integration with other automation systems, controllers, or enterprise software solutions.
5. Sensor Integration
- Integration of advanced sensors and vision systems can enhance the capabilities and flexibility of the robot. Sensors such as cameras, proximity sensors, force/torque sensors, and 3D scanners enable the robot to detect objects, measure distances, and adapt its movements based on real-time feedback.
- Businesses should consider the compatibility and ease of integration of sensors with the chosen robot platform to enable advanced functionalities such as object detection, localization, tracking, and quality inspection.
6. Manufacturer Support and Service
- Choosing a robot from a reputable manufacturer with a track record of reliability, innovation, and customer support is essential. Manufacturers that offer comprehensive service and support, including technical assistance, training programs, spare parts availability, and warranty coverage, can help minimize downtime and ensure long-term success with the automation system.
- Researching customer reviews, testimonials, and case studies can provide insights into the reputation and reliability of different robot manufacturers and models, aiding in the decision-making process.
7. Cost and Return on Investment (ROI)
- Finally, businesses should carefully evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) and expected return on investment (ROI) of the chosen robot. This involves considering not only the upfront purchase cost but also ongoing operational expenses, maintenance costs, and potential productivity gains.
- Conducting a cost-benefit analysis and ROI calculation can help businesses assess the economic viability of the automation project and justify the investment in robotic technology based on projected savings, efficiency improvements, and competitive advantages.
Pick and place robots have revolutionized the manufacturing landscape by automating repetitive tasks with precision and efficiency. By understanding the components, applications, benefits, and disadvantages of pick and place robots, businesses can make informed decisions when implementing automation systems.
Choosing the right robot tailored to your specific requirements can lead to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved overall production quality, paving the way for a transformative journey towards operational excellence in the industrial automation realm.
That’s the article about Pick and Place Robot: A Comprehensive Guide to Automation of Industry. Hope it is useful!










Leave a Reply
View Comments