alwepo.com, Financial ratios are indispensable tools for evaluating the financial health and performance of businesses across various industries. For manufacturing companies, these ratios play a pivotal role in assessing operational efficiency, profitability, liquidity, and overall financial stability. By analyzing key financial metrics, manufacturing firms can make informed decisions, identify areas for improvement, and drive sustainable growth in a competitive market landscape.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the essential financial ratios that manufacturing companies should focus on to optimize their financial management and enhance their long-term viability.
Liquidity Ratios
Current Ratio
The current ratio measures a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations using its current assets. It is calculated by dividing current assets by current liabilities. A current ratio of 2:1 or higher is generally considered healthy for manufacturing companies, indicating that they have sufficient short-term assets to cover their short-term liabilities comfortably. However, excessively high current ratios may suggest inefficient asset management or underutilization of resources.
Quick Ratio (Acid-Test Ratio)
The quick ratio provides a more stringent assessment of liquidity by excluding inventories from current assets. It focuses on the immediate availability of assets to cover short-term liabilities. A quick ratio of 1:1 or higher is desirable for manufacturing companies, indicating their ability to meet short-term obligations without relying on inventory liquidation. This ratio is particularly important for companies with slow-moving or obsolete inventory.
Efficiency Ratios
Inventory Turnover Ratio
The inventory turnover ratio measures how quickly a company sells and replaces its inventory within a specific period. It is calculated by dividing the cost of goods sold (COGS) by the average inventory value. A higher inventory turnover ratio indicates efficient inventory management and faster product turnover, which can lead to reduced carrying costs and improved cash flow. Manufacturing companies should strive to optimize their inventory turnover ratio to minimize excess inventory and avoid stockouts.
Asset Turnover Ratio
The asset turnover ratio evaluates how efficiently a company utilizes its assets to generate revenue. It is calculated by dividing net sales by average total assets. A higher asset turnover ratio suggests better asset utilization and effective management of production capacity. Manufacturing companies should aim to maximize their asset turnover ratio by investing in productive assets, streamlining production processes, and eliminating inefficiencies.
Profitability Ratios
Gross Profit Margin
The gross profit margin measures the percentage of revenue retained by a company after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS). It is calculated by dividing gross profit by net sales and multiplying by 100. A higher gross profit margin indicates better pricing strategies, cost control measures, and efficiency in production. Manufacturing companies can enhance their gross profit margin by optimizing production processes, negotiating better supplier contracts, and reducing wastage.
Net Profit Margin
The net profit margin measures the percentage of revenue that translates into net income after deducting all expenses, including operating costs, taxes, and interest payments. It is calculated by dividing net income by net sales and multiplying by 100. A higher net profit margin signifies strong profitability and effective cost management. Manufacturing companies should focus on improving their net profit margin by reducing operating expenses, enhancing operational efficiency, and diversifying revenue streams.
Financial Stability Ratios
Debt-to-Equity Ratio
The debt-to-equity ratio compares a company’s total debt to its shareholders’ equity, reflecting its reliance on debt financing. It is calculated by dividing total debt by shareholders’ equity. A lower debt-to-equity ratio indicates lower financial risk and greater financial stability. Manufacturing companies should maintain a balanced debt-to-equity ratio to avoid excessive leverage and ensure sustainable growth.
Interest Coverage Ratio
The interest coverage ratio assesses a company’s ability to meet interest payments on its debt obligations. It is calculated by dividing earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) by interest expense. A higher interest coverage ratio indicates better financial health and lower default risk. Manufacturing companies should aim for a comfortable interest coverage ratio to safeguard against financial distress and maintain investor confidence.
Conclusion
In conclusion, monitoring key financial ratios is essential for manufacturing companies to evaluate their financial performance, identify areas for improvement, and make informed strategic decisions. By analyzing liquidity, efficiency, profitability, and financial stability metrics, manufacturing firms can enhance their operational efficiency, maximize profitability, and sustain long-term growth in a competitive market environment. Incorporating these financial ratios into financial analysis and decision-making processes enables manufacturing companies to mitigate risks, capitalize on opportunities, and achieve their business objectives effectively.




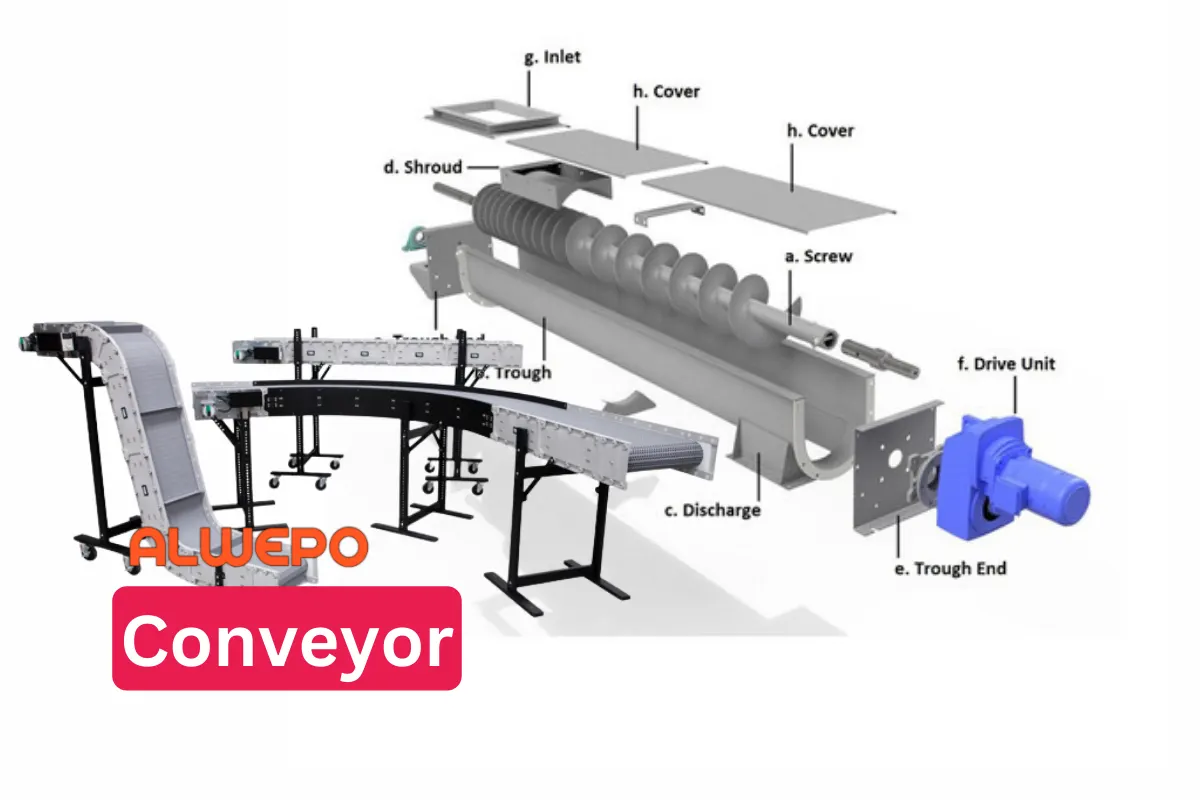





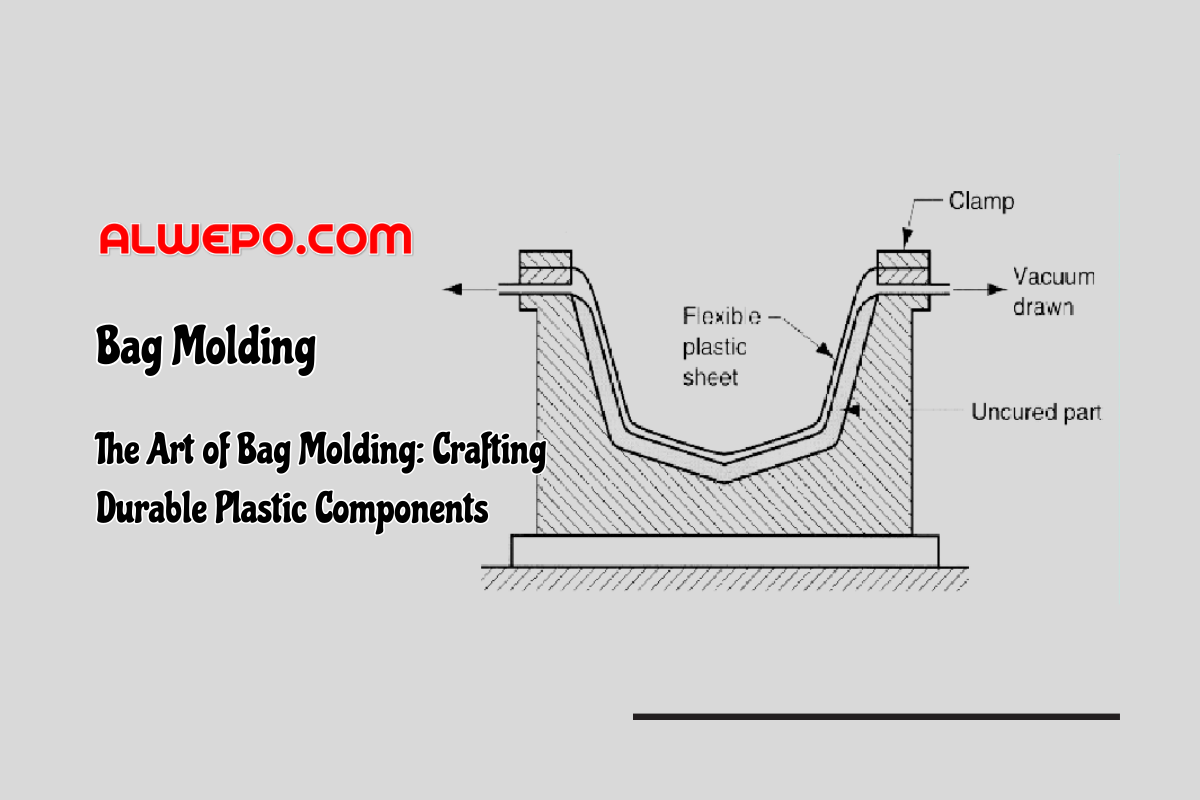


Leave a Reply
View Comments