alwepo.com, Injection Molding Types – Injection molding is a critical process in the manufacturing industry, and one of the key components of this process is the selection of the appropriate gate design. The gate serves as the entry point for molten plastic into the mold cavity, controlling the flow of material and ultimately influencing the quality, appearance, and performance of the final product.
In this article, we will explore various types of injection molding gates and their applications in the manufacturing process.
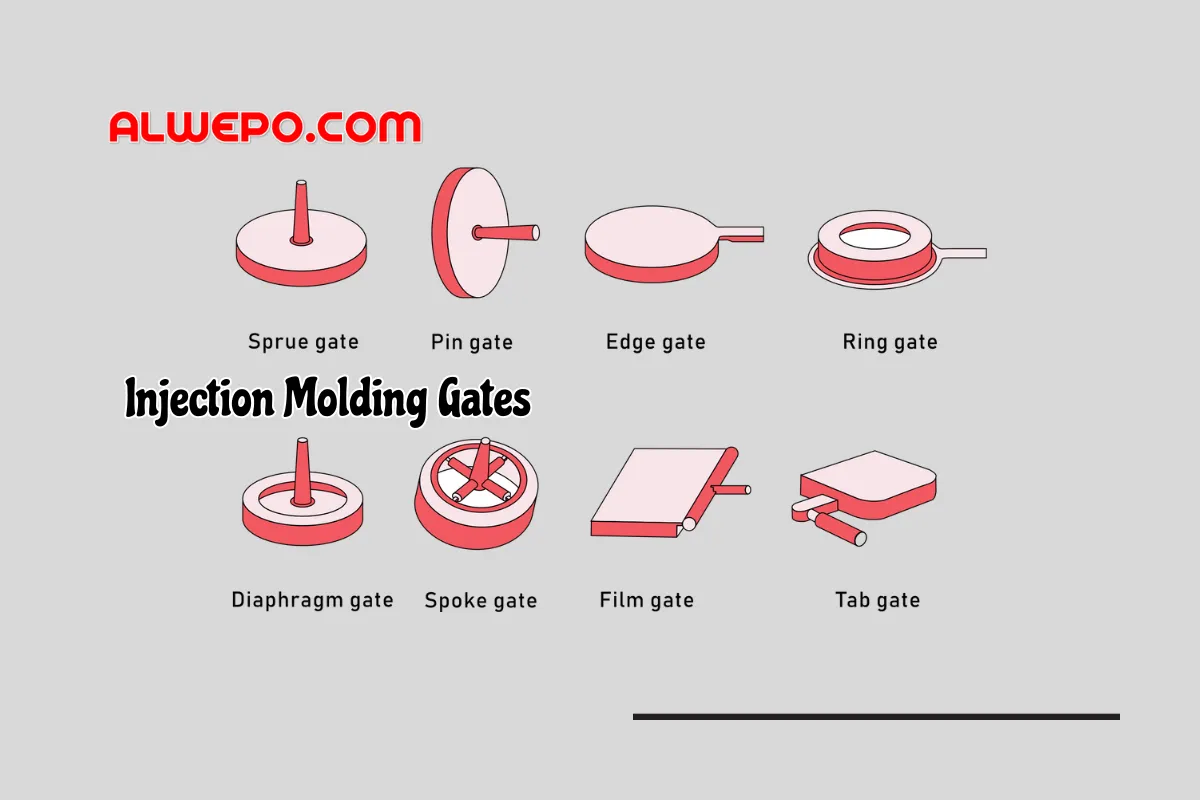
What Is an Injection Molding Gate?
An injection molding gate is a crucial element in the mold design, as it determines how the molten plastic is introduced into the mold cavity. The gate plays a vital role in ensuring uniform filling of the mold, minimizing defects, and optimizing the production of high-quality plastic components. There are several gate designs available, each with its unique characteristics and benefits. Proper gate selection and placement are essential for achieving the desired results in injection molding.
Choosing an Injection Molding Gate
When selecting a gate type and location for a molded part, several factors must be considered. The design of the mold, part orientation, show surface location, and material selection all play a role in determining the appropriate gate design. Additionally, the size and volume of the part, as well as production requirements, must be taken into account when choosing a gate type.
Some plastics are more susceptible to overheating, known as shear heating, which occurs when the plastic is forced through a restricted area. Improper gate design can lead to excessive shear heating, resulting in degraded plastic and incomplete filling of the part. It is essential to choose a gate design that can accommodate the size and volume of the part while maintaining optimal flow and minimizing shear heating.
Common Injection Molding Gate Types
Injection molding gates serve as the entry points for molten plastic into the mold cavity, playing a critical role in the manufacturing process. Each gate type offers distinct advantages and is suited for specific applications. Let’s delve into the details of the most common injection molding gate types:
1. Edge Gate
- Advantages: Edge gates are renowned for their simplicity and effectiveness in the injection molding process. They are easy to produce and modify, making them ideal for filling larger parts or parts with thicker wall sections.
- Applications: Edge gates are commonly used in situations where simplicity and ease of production are paramount. They are suitable for a wide range of parts, including those with complex geometries.
2. Tunnel/Submarine Gate
- Advantages: Tunnel gates are machined below the parting line and are automatically trimmed during ejection. They offer a clean appearance on the finished part surface and are commonly used for small parts or high cavitation molds.
- Applications: Tunnel gates are ideal for parts where gate visibility or appearance is a concern. They are frequently used in applications where gate vestige must be minimized.
3. Cashew Gate
- Advantages: Similar to tunnel gates, cashew gates are machined below the parting line and are automatically sheared during ejection. They are designed to place the injection location behind or below a show surface, minimizing gate visibility.
- Applications: Cashew gates are suitable for parts with specific aesthetic requirements, where gate placement must be discreet to maintain the desired appearance.
4. Direct Sprue Gate
- Advantages: The direct sprue gate is located at the thickest section of the part, allowing for efficient and direct flow of the molten material into the mold. It offers excellent flow characteristics and minimal shear heating.
- Applications: Direct sprue gates are commonly used for parts with uniform wall thicknesses, where efficient material flow and minimal part distortion are essential.
5. Diaphragm Gate
- Advantages: Diaphragm gates are designed for parts with a large open diameter in the middle, ensuring even plastic flow and consistent shrinkage during cooling. They offer uniform filling and reduced warpage.
- Applications: Diaphragm gates are ideal for parts such as disks or circular components where balanced filling and minimal distortion are critical.
6. Hot Runner – Thermal Gate
- Advantages: Hot runner systems, including thermal gates, maintain the molding material molten between the machine barrel and the part. They offer efficient material flow with minimal waste and reduced cycle times.
- Applications: Thermal gates are suitable for high-volume production runs where minimizing material waste and optimizing cycle times are priorities.
7. Hot Runner – Valve Gate
- Advantages: Valve gated hot runner systems provide precise control over the flow of plastic into the cavity, reducing gate vestige and improving process control. They offer superior cosmetic appearance and part quality.
- Applications: Valve gates are commonly used for parts with strict cosmetic requirements or dimensional tolerances, where gate vestige must be minimized, and precise flow control is necessary.
The selection of the appropriate gate design is crucial in injection molding, as it directly impacts the quality and performance of the final product. By understanding the different types of gates available and their applications, manufacturers can make informed decisions to optimize their production processes. Proper gate selection and placement are essential for achieving uniform filling of the mold, minimizing defects, and producing high-quality plastic components.







.webp)




Leave a Reply
View Comments