alwepo.com, Expendable mold casting is a manufacturing process where a mold is made from a disposable material, like sand, plaster, ceramic, or shell, to cast a metal or plastic part. After finishing the casting process, the mold is broken or removed. This is what makes it “expendable” because the mold cannot be used again for future castings.
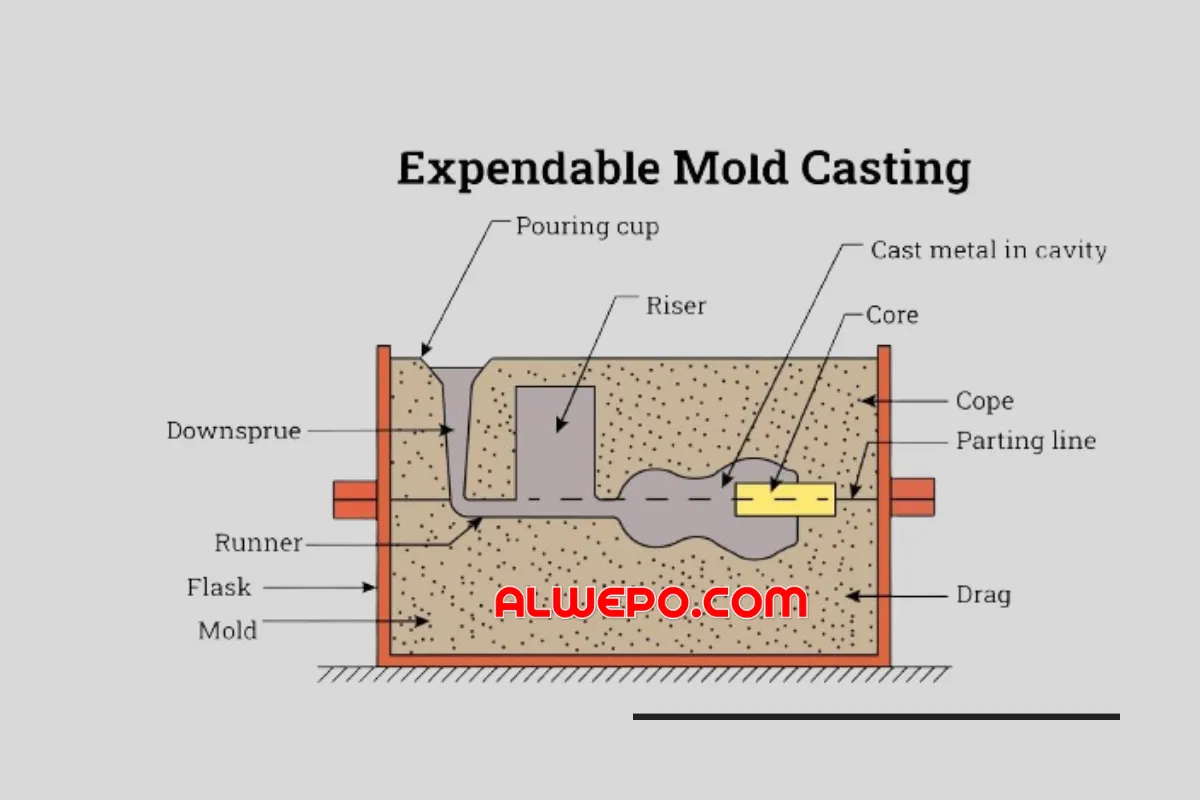
1. Sand Casting
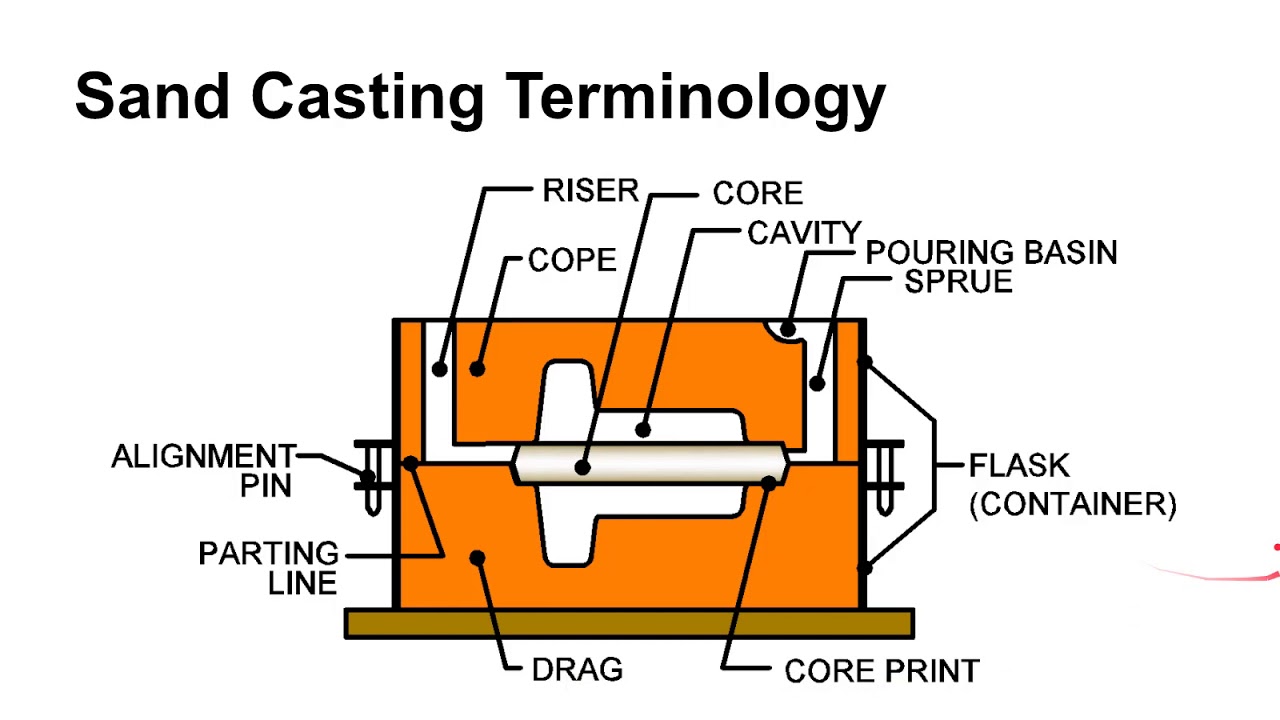
Sand casting is one of the oldest and most versatile forms of expendable mold casting. The process involves creating a mold cavity by compacting specially formulated sand around a pattern (a replica of the desired part). The pattern is then removed, leaving behind the mold cavity. Molten metal is poured into the cavity, where it solidifies to form the final part. After the metal cools and solidifies, the sand mold is broken away to reveal the casting.
Advantages of Sand Casting
- Versatility: Sand casting can accommodate a wide range of shapes and sizes, making it suitable for various applications.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The materials used in sand casting are relatively inexpensive, making it a cost-effective option for low to medium volume production runs.
- Complex Geometry: Sand casting can produce parts with intricate and complex geometries.
- Materials Compatibility: It is compatible with a variety of metals and alloys, including aluminum, iron, steel, and brass.
Disadvantages of Sand Casting
- Surface Finish: Sand casting typically results in rougher surface finishes compared to other casting methods, necessitating additional finishing processes.
- Dimensional Accuracy: Achieving tight dimensional tolerances can be challenging with sand casting.
- Mold Preparation: The process of creating the sand mold can be labor-intensive and time-consuming.
- Environmental Impact: Sand casting generates waste sand, which must be disposed of properly, posing environmental concerns.
Applications Of Sand Casting
- Automotive Industry: Sand casting is extensively used in the automotive sector for producing engine blocks, cylinder heads, transmission cases, and various other components. Its versatility allows for the manufacturing of complex shapes required in engine and transmission systems.
- Aerospace Industry: Sand casting finds applications in the aerospace industry for producing components like turbine blades, engine housings, and structural parts. Its ability to handle high-temperature alloys makes it suitable for aerospace applications.
- Industrial Machinery: Sand casting is utilized in the production of heavy machinery components such as pump housings, valve bodies, and hydraulic cylinders. Its cost-effectiveness and suitability for large parts make it favorable in this sector.
- Construction: Sand casting is employed in the construction industry for manufacturing architectural elements, decorative fixtures, and structural components like columns and beams.
- Art and Sculpture: Sand casting is also used in the creation of artistic sculptures and statues due to its ability to capture intricate details and produce unique shapes.
2. Plaster Casting
Plaster casting, also known as investment casting or plaster mold casting, involves creating a mold using plaster of Paris mixed with water. The mold is formed by pouring the plaster mixture around a pattern, which is then removed once the plaster sets. Molten metal is then poured into the mold cavity, where it solidifies to form the final part. After the metal cools, the plaster mold is broken away to reveal the casting.
Advantages Of Plaster Casting
- Fine Detail: Plaster casting can produce parts with intricate details and smooth surface finishes.
- Low Cost: Plaster is relatively inexpensive compared to other mold materials, making it a cost-effective option for small-scale production.
- Quick Setting Time: Plaster sets relatively quickly, allowing for faster production cycles compared to some other casting methods.
Disadvantages Of Plaster Casting
- Limited to Low Melting Metals: Plaster casting is typically limited to casting metals with low melting points, such as aluminum, zinc, and tin.
- Fragility: Plaster molds are fragile and can break easily, limiting their durability and reusability.
- Surface Porosity: Plaster molds can result in castings with surface porosity, affecting the quality of the final part.
Applications Of Plaster Casting
- Artistic and Decorative Objects: Plaster casting is commonly used in the production of art pieces, sculptures, and decorative objects due to its ability to capture fine details and produce smooth surfaces. It is favored by artists and craftsmen for its versatility and ease of use.
- Prototype Development: Plaster casting is often used in rapid prototyping processes to create prototypes for product development and design validation. Its quick setting time allows for fast iterations and adjustments during the prototyping phase.
- Dental Industry: Plaster casting finds applications in the dental industry for creating dental models, crowns, and prosthetics. Its ability to produce accurate and detailed replicas of dental structures makes it valuable in this field.
3. Ceramic Mold Casting
Ceramic mold casting, also known as ceramic shell casting, involves creating a mold using a ceramic slurry. The process begins with dipping a pattern into the slurry multiple times to build up a ceramic shell around it. Once the shell is sufficiently thick, it is dried and fired to remove the pattern and harden the shell. Molten metal is then poured into the ceramic shell, where it solidifies to form the casting. After the metal cools, the ceramic shell is broken away to reveal the casting.
Advantages Of Ceramic Mold Casting
- High Dimensional Accuracy: Ceramic mold casting can produce parts with tight dimensional tolerances and excellent surface finishes.
- Versatility: It is suitable for casting a wide range of metals and alloys, including steel, bronze, and titanium.
- Minimal Finishing Required: Ceramic molds produce castings with smooth surface finishes, reducing the need for additional finishing operations.
Disadvantages Of Ceramic Mold Casting
- Complex Process: Ceramic mold casting involves multiple steps and can be time-consuming and labor-intensive.
- High Cost: The materials and equipment required for ceramic mold casting can be expensive, making it less cost-effective for low-volume production.
- Limited Mold Reusability: Ceramic molds are fragile and can only be used for a limited number of castings before they need to be replaced.
Applications Of Ceramic Mold Casting
- Aerospace and Defense: Ceramic mold casting is widely used in the aerospace and defense industries for producing components like turbine blades, aerospace engine parts, and missile components. Its ability to maintain dimensional accuracy and produce intricate shapes makes it suitable for critical aerospace applications.
- Industrial Machinery: Ceramic mold casting is employed in the manufacturing of industrial machinery components such as pump impellers, valve bodies, and hydraulic components. Its high dimensional accuracy and surface finish contribute to the performance and reliability of industrial machinery.
- Medical Devices: Ceramic mold casting finds applications in the medical device industry for producing components like surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, and medical device housings. Its biocompatibility and precision make it suitable for medical applications where accuracy and quality are paramount.
4. Shell Mold Casting
Shell mold casting is similar to sand casting but uses a resin-coated sand mixture to create the mold. The process involves creating a mold cavity by compacting resin-coated sand around a pattern. Once the sand mixture sets, it forms a rigid shell around the pattern. Molten metal is then poured into the shell mold, where it solidifies to form the casting. After the metal cools, the shell mold is broken away to reveal the casting.
Advantages Of Shell Mold Casting
- High Dimensional Accuracy: Shell mold casting can achieve tight dimensional tolerances and produce parts with excellent surface finishes.
- Shorter Production Cycle: The resin-coated sand sets relatively quickly, allowing for faster production cycles compared to traditional sand casting.
- Versatility: Shell mold casting is suitable for casting a wide range of metals and alloys, including iron, steel, and aluminum.
Disadvantages Of Shell Mold Casting
- Cost: The resin-coated sand used in shell mold casting can be more expensive than traditional sand casting materials, increasing production costs.
- Limited Mold Reusability: Shell molds have a limited lifespan and can only be used for a certain number of castings before they degrade and need to be replaced.
- Environmental Impact: The resin used in shell mold casting can emit harmful fumes during the casting process, posing environmental concerns.
Applications Of Shell Mold Casting
- Automotive Industry: Shell mold casting is extensively used in the automotive sector for producing components like cylinder heads, intake manifolds, and gearbox housings. Its ability to achieve tight dimensional tolerances and produce fine surface finishes meets the stringent requirements of automotive applications.
- Consumer Goods: Shell mold casting finds applications in the production of consumer goods such as household appliances, power tools, and sporting equipment. Its ability to produce complex shapes and high-quality surface finishes enhances the aesthetic appeal and functionality of consumer products.
- Electronics Industry: Shell mold casting is utilized in the electronics industry for manufacturing components like heat sinks, electronic enclosures, and connector housings. Its precision and repeatability ensure the reliability and performance of electronic devices.
5. Vacuum Casting
Vacuum casting, also known as vacuum-assisted casting, involves creating a mold using a two-part silicone rubber material. The process begins with placing a master pattern (a replica of the desired part) into a casting box. The silicone rubber is then mixed and poured over the pattern, covering it completely. A vacuum chamber is used to remove air bubbles from the silicone rubber, ensuring a precise mold. Once the silicone sets, the master pattern is removed, leaving behind a mold cavity. Molten resin is then poured into the mold under vacuum pressure, where it fills the cavity and solidifies to form the casting.
Advantages Of Vacuum Casting
- High Reproduction Accuracy: Vacuum casting can produce parts with precise details and dimensional accuracy, faithfully replicating the master pattern.
- Fast Prototyping: Vacuum casting is commonly used for rapid prototyping and small-scale production due to its quick turnaround times.
- Variety of Materials: It is compatible with a wide range of casting materials, including urethane resins, polyurethanes, and silicones.
Disadvantages Of Vacuum Casting
- Limited to Low-Volume Production: Vacuum casting is more suitable for small to medium volume production runs and may not be cost-effective for large-scale manufacturing.
- Material Limitations: The choice of casting materials for vacuum casting is somewhat limited compared to other casting methods.
- Mold Durability: Silicone rubber molds used in vacuum casting have a limited lifespan and may degrade over time with repeated use.
Applications Of Vacuum Casting
- Prototyping: Vacuum casting is commonly used in rapid prototyping processes for creating prototypes of products and components. Its ability to produce accurate and detailed replicas allows designers and engineers to evaluate designs and test functionalities before mass production.
- Small Batch Production: Vacuum casting is suitable for small batch production runs where cost-effectiveness and fast turnaround times are important. It allows manufacturers to produce limited quantities of parts without investing in expensive tooling or equipment.
- Custom Manufacturing: Vacuum casting is utilized in custom manufacturing applications where each part may have unique specifications or design requirements. It offers flexibility in producing customized parts tailored to individual customer needs.
Expendable mold casting encompasses a variety of methods, each offering unique advantages and limitations. Understanding the characteristics and processes of sand casting, plaster casting, ceramic mold casting, shell mold casting, and vacuum casting can help manufacturers choose the most suitable method for their specific requirements and production needs. By leveraging the strengths of each casting method, industries can efficiently produce high-quality parts for various applications.
That’s the article about Expendable mold casting. Don’t forget to share it on your favorite social media, and hopefully it’s useful!


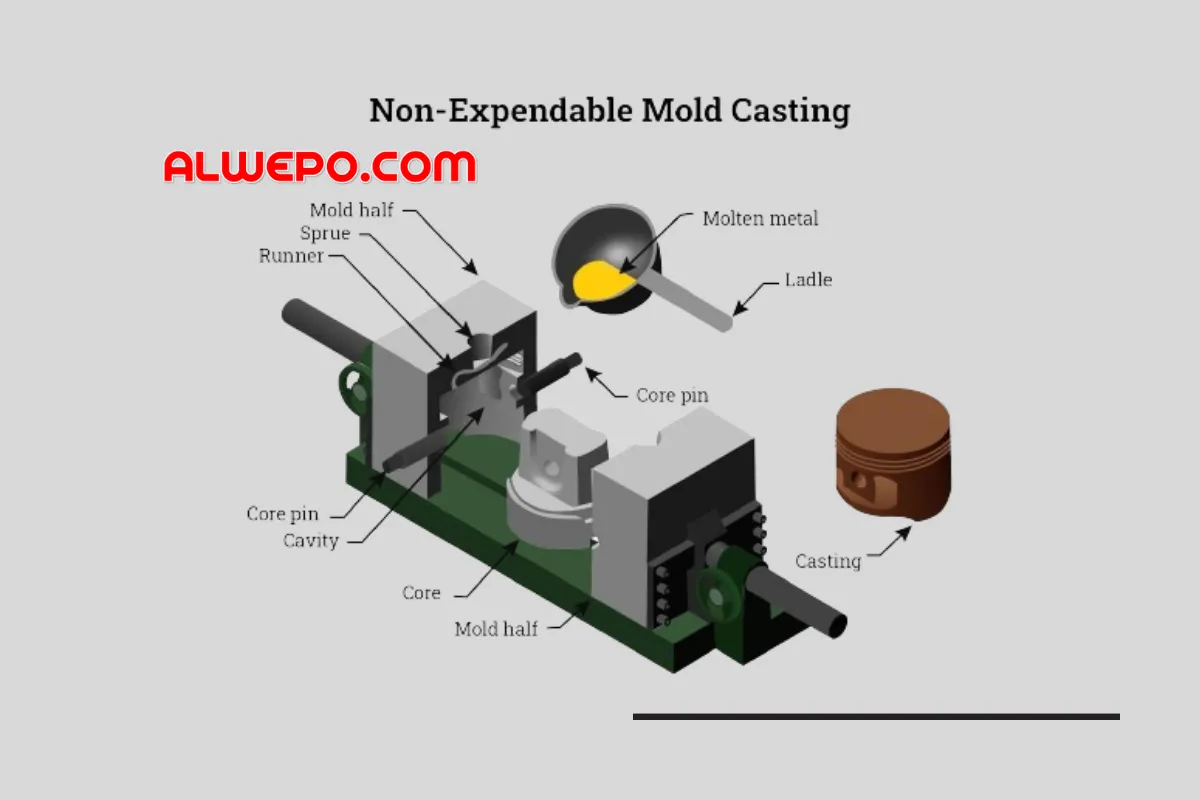

.jpg)


.jpg)




Leave a Reply
View Comments