alwepo.com, Autonomous Mobile Robots – The logistics and warehousing industry is undergoing one of its most significant transformations in decades. As global e-commerce expands, supply chains become more complex, and customer expectations for fast delivery continue to grow, warehouses face increasing pressure to optimize operations. In response, many companies are turning to Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)—intelligent, flexible robots capable of navigating dynamic environments without fixed paths or manual control.
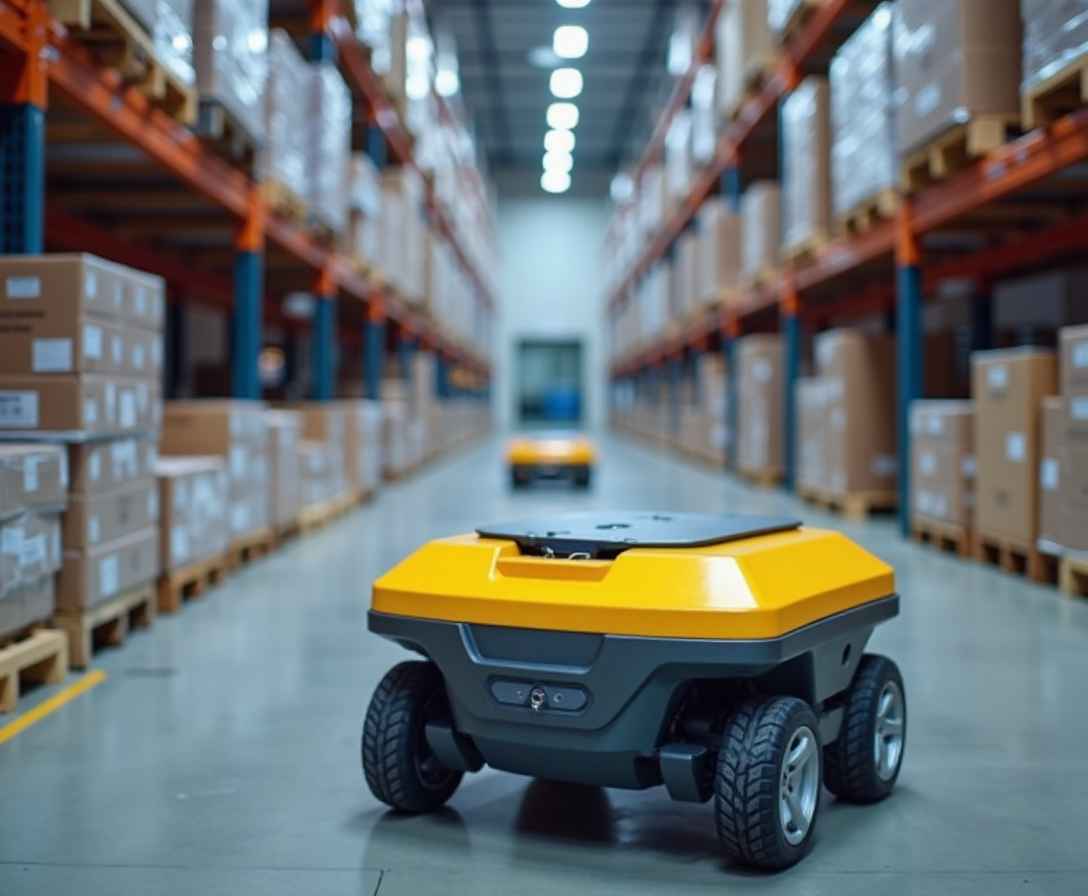

AMRs represent the next evolution of robotics in logistics. Unlike Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), which rely on tracks, wires, or magnetic strips, AMRs use advanced sensors, AI algorithms, and real-time mapping to move freely and safely across warehouse floors. Their rapid growth is reshaping warehouse layouts, labor strategies, productivity benchmarks, and fulfillment processes on a global scale.
This article explores the rise of AMRs in warehouses, key technologies driving them, their benefits, use cases, market trends, challenges, and what the future of warehouse automation looks like.
What Are Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)?
AMRs are self-navigating robots designed to transport goods within a facility. They make intelligent, real-time decisions using:
-
LIDAR sensors
-
Cameras
-
3D mapping technology
-
AI-driven navigation algorithms
-
Obstacle avoidance systems
Unlike traditional robotics that require predefined routes, AMRs adjust their paths autonomously to avoid barriers and optimize travel time. This flexibility makes them ideal for modern warehouses where layouts change frequently and human workers share the same workspace.
Why AMRs Are Growing Rapidly in Warehouses
Several factors are accelerating the adoption of AMRs across the global logistics sector.
1. E-Commerce Growth and Need for Faster Fulfillment
Online shopping has exploded, creating higher demand for:
-
Faster order processing
-
Higher picking accuracy
-
Shorter cycle times
AMRs help meet these demands by automating material movement, reducing bottlenecks, and enabling faster order turnaround.
2. Labor Shortages in Warehousing
Warehouses face chronic labor shortages due to:
-
Physically demanding tasks
-
High turnover rates
-
Seasonal spikes in demand
AMRs fill workforce gaps while allowing human workers to focus on skilled tasks such as quality checks, equipment maintenance, and advanced decision-making.
3. Rising Wage and Operating Costs
Automation reduces operational expenses by minimizing:
-
Overtime pay
-
Manual transportation labor
-
Downtime from fatigue or injury
Over time, AMRs provide a high ROI, especially for large distribution centers.
4. Need for Operational Flexibility
Modern warehouses must adapt quickly to:
-
New product categories
-
Sudden demand fluctuations
-
Layout changes
AMRs adapt instantly through software updates—no physical infrastructure changes are required.
5. Industry 4.0 and Digital Transformation
AMRs are a core component of smart warehousing initiatives using:
-
IoT sensors
-
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
-
Real-time data analytics
-
Cloud connectivity
This creates an intelligent, connected ecosystem that improves efficiency and accuracy.
How AMRs Work: Key Technologies Behind Autonomous Navigation
AMRs combine several advanced technologies that enable safe and efficient operation.
1. Sensor Fusion and Perception Technology
AMRs use sensors such as:
-
LIDAR for environment mapping
-
Cameras for visual recognition
-
Ultrasonic sensors for proximity detection
-
Infrared sensors for object detection
These devices work together to create a real-time understanding of the warehouse environment.
2. Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM)
SLAM technology allows AMRs to:
-
Build internal maps of warehouses
-
Localize their position accurately
-
Update maps in real time
-
Navigate without physical guides
SLAM is a major reason AMRs can operate in dynamic facilities.
3. AI-Based Path Planning
Machine learning algorithms help AMRs:
-
Choose the most efficient routes
-
Avoid congestion
-
Predict human movement patterns
-
Adapt to layout changes
This AI-driven approach minimizes delays and traffic jams.
4. Fleet Management Software
Fleet management systems coordinate:
-
Traffic flow
-
Task assignments
-
Charging schedules
-
Maintenance alerts
This ensures multiple AMRs work together seamlessly.
5. Connectivity and IoT Integration
AMRs communicate with:
-
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
-
ERP systems
-
IoT sensors
-
Cloud platforms
This enables real-time decision-making and full visibility into operations.
Benefits of Implementing AMRs in Warehouses
AMRs deliver a wide range of advantages that traditional manual or semi-automated systems cannot match.
1. Increased Productivity
AMRs automate repetitive material handling tasks, allowing humans to focus on:
-
Picking
-
Packing
-
Quality control
This boosts overall throughput and reduces cycle time.
2. Improved Accuracy and Reduced Errors
AMRs minimize:
-
Misplaced items
-
Picking errors
-
Manual handling mistakes
This is essential for industries requiring high accuracy, such as pharmaceuticals and electronics.
3. Enhanced Safety
Warehouse tasks can be physically demanding and prone to injury. AMRs improve safety by:
-
Reducing heavy lifting
-
Eliminating long walking distances
-
Detecting and avoiding obstacles
Their built-in safety systems prevent collisions with people or equipment.
4. Reduced Labor Dependency
AMRs fill labor gaps caused by:
-
Staffing shortages
-
High turnover
-
Seasonal peaks
They ensure stable workflows regardless of labor market conditions.
5. Scalability
AMRs can be deployed incrementally. Companies can start with a few units and scale up as needed—without major infrastructure changes.
6. Lower Operational Costs
Savings come from:
-
Reduced manual labor
-
Less downtime
-
More efficient workflows
-
Fewer workplace injuries
-
Lower training costs
Over time, AMRs typically provide a strong ROI.
Types of AMRs Used in Warehouses
There are several categories of AMRs depending on their function.
1. Goods-to-Person (G2P) AMRs
These robots transport shelving units or totes directly to human pickers. They reduce walking time and boost picking speed significantly.
2. Tote-Handling AMRs
These robots carry individual totes or bins between stations during order fulfillment.
3. Pallet-Handling AMRs
Designed to lift and transport full pallets, they automate heavy logistics tasks traditionally handled by forklifts.
4. Sorting AMRs
Used in distribution centers, these robots sort packages based on shipping labels, size, and destination.
5. Inventory Scanning AMRs
Equipped with scanners and cameras, they perform autonomous:
-
Inventory counts
-
Shelf checks
-
Stock visibility updates
This improves inventory accuracy dramatically.
6. Autonomous Forklifts
These are advanced AMRs capable of performing forklift operations such as:
-
Pallet picking
-
Rack storage
-
High-level stacking
They reduce accidents and improve efficiency in palletized warehousing.
Industries Using AMRs in Warehouses
AMRs are being adopted across multiple sectors such as:
-
E-commerce and retail
-
Automotive
-
Electronics
-
Pharmaceuticals
-
Food and beverage
-
Healthcare logistics
-
Third-party logistics (3PL)
-
Consumer goods
Their flexibility makes them suitable for both small facilities and mega-distribution centers.
Real-World Use Cases of AMRs in Warehouses
1. Amazon: Large-Scale AMR Deployment
Amazon uses tens of thousands of AMRs (formerly Kiva robots) to automate goods-to-person picking, reducing processing time by nearly 50%.
2. DHL: AMRs for Picking Assistance
DHL uses AMRs to assist human pickers by transporting goods, improving productivity and reducing walking fatigue.
3. Walmart: Inventory Scanning Robots
Walmart deploys AMRs for stock monitoring, providing real-time inventory accuracy.
4. Automotive Warehouses
Manufacturers use AMRs to transport heavy components between production lines and storage, improving efficiency.
5. Pharmaceutical Distribution Centers
AMRs improve accuracy and traceability—critical for regulated industries.
Challenges of Implementing AMRs in Warehouses
While the growth is strong, companies must address several challenges.
1. High Initial Investment
AMRs require investment in:
-
Hardware
-
Software
-
Connectivity infrastructure
-
Workforce training
However, long-term ROI typically offsets upfront costs.
2. Integration with Existing Systems
AMRs must be compatible with:
-
WMS
-
ERP
-
Existing warehouse workflows
Poor integration can reduce efficiency.
3. Cybersecurity Concerns
Connected robots introduce risks of:
-
Hacking
-
Data theft
-
Operational disruption
Proper cybersecurity measures are essential.
4. Workforce Adaptation
Employees must learn:
-
Robot monitoring
-
Basic maintenance
-
Collaboration safety protocols
Change management is critical.
5. Navigation Limitations
AMRs may struggle in:
-
Extremely cluttered environments
-
Facilities with poor lighting
-
High-speed operations requiring precision
Choosing the right AMR type is essential.
The Future of AMRs in Warehousing
1. More Intelligent Navigation with AI
AMRs will increasingly use:
-
Deep learning
-
Predictive obstacle detection
-
Human behavior modeling
This boosts safety and efficiency.
2. Fully Autonomous Fulfillment Centers
Future warehouses may rely on AMRs for:
-
Picking
-
Sorting
-
Packing
-
Transporting
-
Stock counting
Humans will supervise and manage exceptions.
3. Integration with Humanoid Robots
AMRs will work alongside humanoid robots that handle:
-
Dexterous picking
-
Packaging
-
Complex tasks
Automation will be more comprehensive.
4. Expansion of “Robot-as-a-Service” (RaaS)
Companies will rent AMRs on monthly subscriptions, making automation accessible even for SMEs.
5. Advanced Fleet Collaboration
Large fleets will communicate with each other to:
-
Avoid congestion
-
Self-organize
-
Distribute workload intelligently
This creates a highly optimized robotic ecosystem.
6. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Future AMRs will:
-
Use greener batteries
-
Self-optimize energy consumption
-
Operate within eco-friendly warehouses
This aligns with global sustainability goals.
Conclusion: AMRs Are Reshaping the Future of Warehousing
The adoption of Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) is accelerating at a remarkable pace. As warehouses face increasing pressure for speed, accuracy, flexibility, and cost-efficiency, AMRs offer a powerful solution. Their ability to navigate autonomously, work safely alongside humans, and adapt to dynamic environments makes them an essential component of modern logistics.
From e-commerce giants to pharmaceutical distributors, AMRs are transforming how goods are stored, moved, and processed. The future of warehousing is undeniably automated—and AMRs are at the center of this evolution.
Companies that embrace AMRs today will gain:
-
Strong competitive advantages
-
Higher productivity
-
Better accuracy
-
Enhanced worker satisfaction
-
Lower long-term operational costs
The era of smart, automated warehouses has arrived, and AMRs are leading the revolution.