alwepo.com, In manufacturing and machining, Computer Numerical Control (CNC) milling machines stand as the cornerstone of precision and efficiency. These machines come in various configurations, each offering unique capabilities and advantages.
In this comprehensive analysis, we delve into the nuances of 3, 4, and 5-axis CNC milling machines, dissecting their functionalities, applications, and comparative strengths.
Understanding CNC Milling Axes
CNC milling, understanding the concept of milling axes is fundamental to comprehending the capabilities and functionalities of various machining machines. A CNC milling machine operates based on numerical control, where precise instructions are provided to the machine through computer programming to execute specific machining tasks. The number of axes in a CNC milling machine denotes the directions along which the cutting tool and the workpiece can move relative to each other. These axes are pivotal in determining the machine’s versatility, precision, and the types of geometries it can produce.
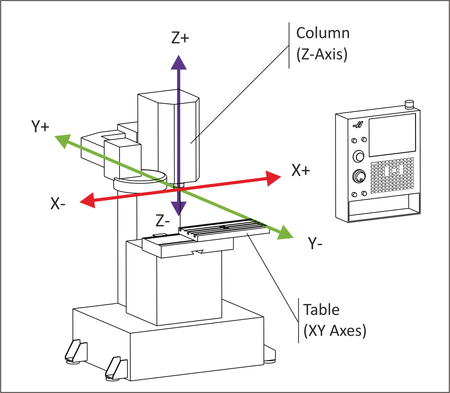
The primary axes found in CNC milling are the X, Y, and Z axes:
- X-Axis: The X-axis represents horizontal movement along the length of the workpiece. In a typical setup, the cutting tool moves along the X-axis while the workpiece remains stationary or moves vertically (Y-axis) and/or depth-wise (Z-axis). Movement along the X-axis enables the machining of features that extend along the length of the workpiece, such as slots, keyways, and flat surfaces.
- Y-Axis: The Y-axis denotes vertical movement along the width of the workpiece. It allows the cutting tool to move vertically, perpendicular to the X-axis. Movement along the Y-axis facilitates the machining of features that extend across the width of the workpiece, such as pockets, holes, and contours.
- Z-Axis: The Z-axis signifies vertical movement along the height of the workpiece. It controls the depth of the cutting tool penetration into the workpiece, enabling operations such as drilling, milling, and profiling. Movement along the Z-axis is essential for creating features with varying depths and complex 3D geometries.
The Versatility of 3-Axis CNC Milling Machines
3-axis CNC milling machines are the most common and widely used in manufacturing industries. They offer a solid foundation for machining various materials with precision and efficiency. The primary advantage of 3-axis machines lies in their simplicity and ease of operation, making them ideal for prototyping, general machining, and production of simple components.
Applications and Advantages
3-axis CNC milling machines find applications across a broad spectrum of industries, including aerospace, automotive, electronics, and medical device manufacturing. Their versatility makes them suitable for producing components such as flat and prismatic parts, molds, dies, and prototypes. Key advantages of 3-axis machines include:
- Cost-effectiveness: 3-axis machines are relatively affordable and require minimal setup and maintenance compared to higher-axis configurations.
- Simplified Programming: The programming of 3-axis machines is straightforward, making them accessible to operators with basic CNC machining knowledge.
- High Accuracy: Despite their simplicity, 3-axis machines can achieve high levels of accuracy and repeatability, meeting the precision requirements of many applications.
Elevating Precision with 4-Axis CNC Milling Machines
4-axis CNC milling machines introduce an additional rotary axis, typically referred to as the A-axis, to the standard X, Y, and Z axes. This rotational axis enables the machining of features on multiple sides of a workpiece without the need for repositioning, enhancing efficiency and precision.
Enhanced Flexibility and Complexity
The inclusion of a fourth axis in CNC milling expands the range of geometries that can be machined, allowing for features such as undercuts, contours, and helical surfaces. This increased flexibility is particularly advantageous in applications requiring intricate 3D machining, such as complex molds, aerospace components, and decorative pieces.
Additionally, 4-axis machines excel in the production of cylindrical parts and components with irregular shapes, thanks to their ability to rotate the workpiece during machining. This rotational capability reduces setup time and eliminates the need for multiple operations, streamlining the manufacturing process.
Unleashing Complexity with 5-Axis CNC Milling Machines
5-axis CNC milling machines represent the pinnacle of machining technology, offering unmatched precision, versatility, and capability. In addition to the standard X, Y, and Z axes, these machines incorporate two rotary axes, typically denoted as A and B axes. This simultaneous movement in multiple directions enables the machining of highly complex geometries with unparalleled accuracy.
Intricate Machining and Advanced Applications
The advanced capabilities of 5-axis CNC milling machines make them indispensable in industries where precision is paramount, such as aerospace, defense, and medical device manufacturing. These machines excel in the production of turbine blades, impellers, aerospace components, and medical implants, where intricate contours and complex geometries are common.
Furthermore, 5-axis machines offer significant advantages in terms of reducing setup time, eliminating the need for multiple fixtures, and improving surface finish quality. By tilting and rotating the workpiece along multiple axes, they can access difficult-to-reach areas and machine features from multiple angles, resulting in superior part accuracy and surface finish.
Conclusion
The choice between 3, 4, and 5-axis CNC milling machines depends on the specific requirements of the application, the complexity of the parts to be machined, and the desired level of precision. While 3-axis machines offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness, 4 and 5-axis machines elevate precision and enable the machining of complex geometries.
Ultimately, manufacturers must carefully evaluate their machining needs and weigh the advantages of each axis configuration to select the most suitable solution for their operations. Whether it’s producing simple components or intricate aerospace parts, CNC milling machines continue to push the boundaries of precision engineering and manufacturing.




.jpg)

.webp)




Leave a Reply
View Comments