alwpeo.com, Types of CNC Machines and Their Control Systems – In manufacturing, Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines have emerged as indispensable tools, revolutionizing the way various industries produce components and products. From automotive to aerospace, CNC machines play a pivotal role in achieving precision, efficiency, and automation in manufacturing processes. Understanding the different types of CNC machines and their associated control systems is essential for manufacturers looking to optimize their production capabilities and stay competitive in today’s market.
Types of CNC Machines
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are advanced manufacturing tools that utilize computer-controlled processes to shape and manipulate various materials with precision and efficiency. These machines come in different types, each designed for specific applications and machining tasks. Let’s explore the various types of CNC machines in detail:
1. CNC Milling Machines
.jpg)
- CNC milling machines are versatile tools used for cutting and shaping solid materials such as metal, wood, and plastics.
- They utilize rotating cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece, producing complex shapes, contours, and surface finishes.
- CNC milling machines come in various configurations, including vertical milling machines, horizontal milling machines, and multi-axis milling machines.
- They are widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and mold making for producing components ranging from engine parts to intricate molds.
2. CNC Turning Machines (Lathes)
.jpg)
- CNC turning machines, also known as lathes, are designed for machining cylindrical parts by rotating the workpiece against stationary cutting tools.
- They are capable of producing a wide range of components, including shafts, pins, and bolts, with high precision and efficiency.
- CNC turning machines are essential in industries such as manufacturing, aerospace, and medical device production.
3. CNC Drilling Machines
.jpg)
- CNC drilling machines are specialized tools used for creating holes in workpieces with precision and accuracy.
- They come in various configurations, including vertical drilling machines, horizontal drilling machines, and multi-spindle drilling machines.
- CNC drilling machines are widely used in industries such as construction, metal fabrication, and electronics manufacturing for creating holes in components ranging from circuit boards to structural steel.
4. CNC Grinding Machines
.jpg)
- CNC grinding machines are used for precision grinding operations to achieve tight tolerances, surface finishes, and dimensional accuracy.
- They utilize abrasive grinding wheels to remove material from a workpiece, producing smooth and precise surfaces.
- CNC grinding machines are commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and toolmaking for grinding components such as gears, bearings, and cutting tools.
5. CNC Routing Machines
.jpg)
- CNC routing machines are specialized tools used for cutting, shaping, and engraving various materials, including wood, plastic, and composites.
- They utilize rotating cutting tools, such as routers and spindle motors, to carve out intricate designs and contours.
- CNC routing machines are popular in industries such as woodworking, signage, and prototyping for creating custom components and prototypes.
6. CNC Plasma and Laser Cutting Machines
.jpg)
- CNC plasma and laser cutting machines are used for cutting metal and other materials with high precision and speed.
- They utilize plasma or laser beams to melt and vaporize material from a workpiece, creating clean and accurate cuts.
- CNC plasma and laser cutting machines are widely used in industries such as metal fabrication, automotive, and signage for cutting components such as sheet metal, plates, and pipes.
CNC Control Systems
CNC control systems serve as the brain of CNC machines, responsible for interpreting design instructions and translating them into precise movements of the cutting tools. These systems consist of hardware components such as control units, motors, and sensors, as well as software components such as programming languages and operating interfaces.
1. Open-Loop Control Systems
- In an open-loop control system, commands are sent to the machine without any feedback mechanism to verify the accuracy of the executed movements.
- These systems rely solely on pre-programmed instructions, making them less precise compared to closed-loop systems.
- Open-loop control systems are suitable for simple machining tasks where high precision is not critical.
2. Closed-Loop Control Systems
- Closed-loop control systems incorporate feedback mechanisms such as encoders, sensors, and servo motors to continuously monitor and adjust machine performance in real-time.
- These systems provide enhanced accuracy and precision by compensating for errors and deviations during machining operations.
- Closed-loop control systems are ideal for applications requiring high precision and tight tolerances, such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing.
3. Hybrid Control Systems
- Hybrid control systems combine elements of both open-loop and closed-loop control systems to achieve a balance between performance and cost-effectiveness.
- These systems utilize feedback mechanisms for critical operations while relying on pre-programmed instructions for less demanding tasks.
- Hybrid control systems offer versatility and flexibility, making them suitable for a wide range of machining applications in various industries.
4. Adaptive Control Systems
- Adaptive control systems use real-time data from sensors and monitoring devices to adjust machining parameters dynamically.
- By continuously optimizing cutting conditions based on changing factors such as workpiece properties and tool wear, adaptive control systems improve machining accuracy and efficiency.
- These systems are particularly beneficial for complex machining tasks where maintaining consistent quality is crucial.
5. Cloud-Based Control Systems
- Cloud-based control systems enable remote monitoring, programming, and troubleshooting of CNC machines via internet connectivity.
- Operators can access machine data and control functions from anywhere with an internet connection, facilitating collaboration and flexibility in manufacturing operations.
- Cloud-based control systems offer scalability and accessibility, allowing manufacturers to optimize workflows and resource utilization.
6. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integrated Systems
- AI-integrated control systems leverage machine learning algorithms to optimize machining processes, predict tool wear, and automate toolpath generation.
- By analyzing large datasets and learning from past experiences, AI systems can make data-driven decisions to improve machining efficiency and productivity.
- These systems represent the next frontier in CNC control technology, offering unprecedented levels of automation and intelligence in manufacturing operations.
Conclusion
Understanding the diverse types of CNC machines and their control systems is essential for manufacturers seeking to optimize their production processes and achieve superior quality and efficiency. Whether it’s CNC milling machines, turning machines, or drilling machines, each type offers unique capabilities and advantages for various machining applications.
Likewise, CNC control systems, including CNC control units and motion control technologies, play a crucial role in ensuring precise and reliable operation of CNC machines. By leveraging the right combination of CNC machines and control systems, manufacturers can unlock new possibilities in manufacturing and stay ahead in today’s competitive market landscape.


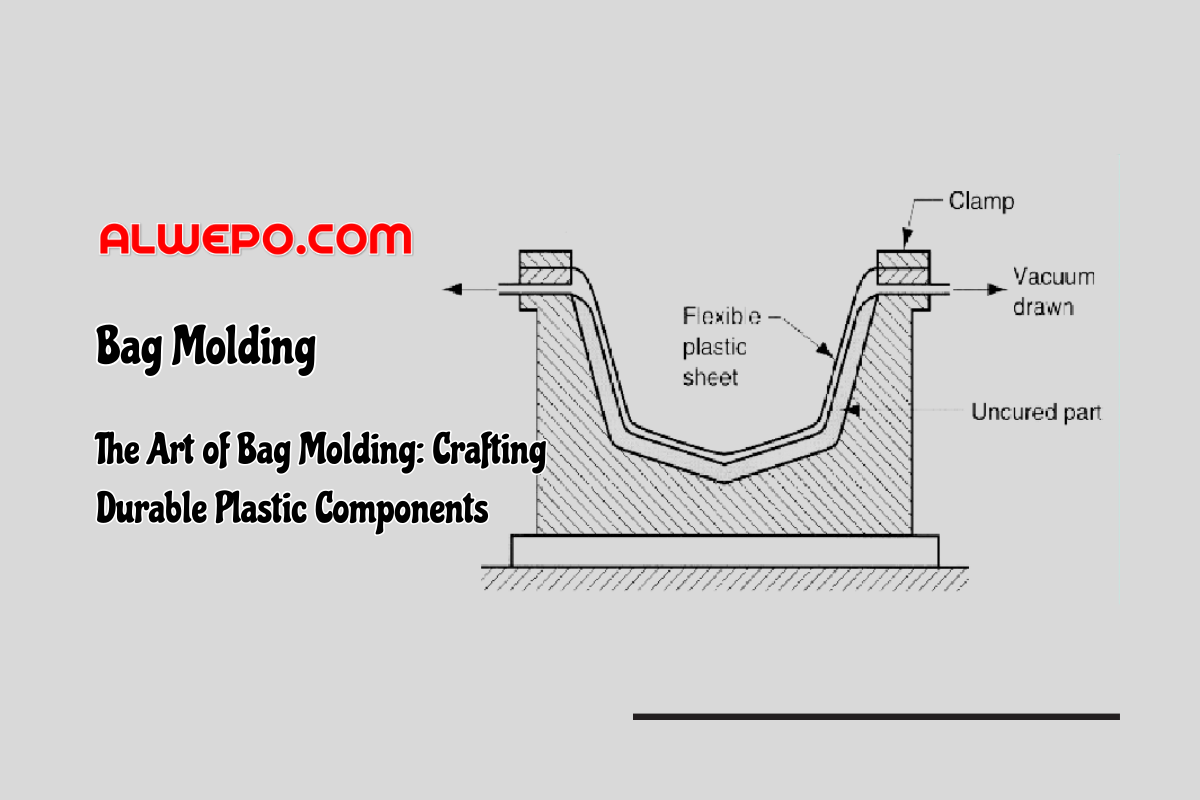
.jpg)









Leave a Reply
View Comments