Hello Alwepo friends, in this article, we will explore the world of ERP Software for Manufacturing Industry. ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software is a powerful solution that integrates various business processes, from production and inventory management to human resources and finance. In the fast-paced and competitive manufacturing sector, implementing the right ERP system can make all the difference in optimizing operations, improving efficiency, and achieving sustainable growth.
What is ERP Software?

a. Defining ERP Software:
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning. ERP software is a sophisticated and centralized business management system that integrates various core processes and functions of an organization into a single unified platform. It serves as a backbone for information flow, data sharing, and process automation across different departments within a company.
The primary objective of ERP software is to enhance overall efficiency, productivity, and visibility of the organization by providing real-time access to critical data and streamlining business processes. It eliminates the need for disparate, standalone systems and instead provides a centralized database that can be accessed and utilized by various departments, fostering better communication and collaboration between teams.
b. The Core Components of ERP:
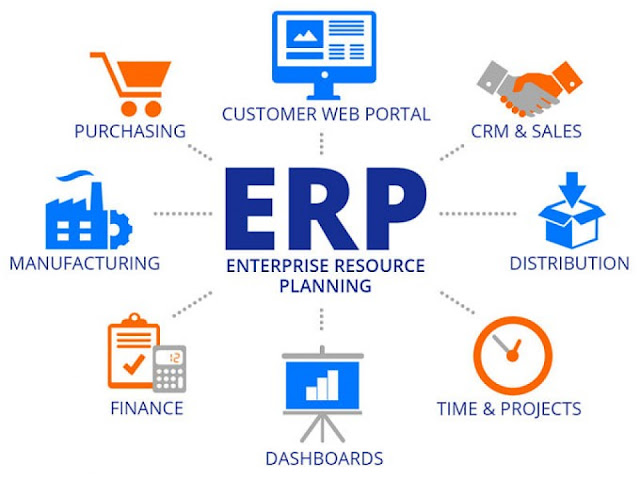
ERP software consists of several modules, each catering to a specific aspect of business operations. Some of the core components/modules commonly found in ERP systems include:
- Manufacturing: This module assists in managing the manufacturing process, including production planning, scheduling, work orders, and material requirements planning (MRP).
- Supply Chain Management: The SCM module focuses on optimizing the supply chain by handling procurement, inventory management, supplier relationships, and order fulfillment.
- Finance: The finance module handles accounting, financial reporting, budgeting, accounts payable and receivable, general ledger, and other financial aspects of the organization.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): This module is dedicated to managing customer-related activities, such as sales, marketing, customer support, and service management.
- Human Resources (HR): The HR module deals with employee information, payroll processing, benefits administration, performance management, and other HR-related functions.
- Inventory Management: This module is specifically focused on optimizing inventory levels, tracking stock movements, and maintaining accurate stock records.
- Business Intelligence (BI) and Reporting: The BI module provides analytical tools and customizable reports to help management make informed decisions based on real-time data.
c. Advantages of ERP Software for Manufacturers:
- Streamlined Operations: ERP software brings together different processes like production planning, scheduling, inventory management, and more, into a cohesive system. This streamlines operations, reduces duplication of effort, and enhances overall productivity.
- Enhanced Collaboration: With data accessible across departments, ERP fosters collaboration and communication between teams. Information sharing becomes more efficient, leading to better cross-functional coordination.
- Improved Data Accuracy: Manual data entry and disparate systems can lead to errors. ERP software centralizes data and automates processes, reducing the risk of data inaccuracies and ensuring data integrity.
- Better Decision-Making: ERP provides real-time insights into various aspects of the manufacturing process, enabling management to make data-driven decisions quickly and effectively.
- Regulatory Compliance: ERP systems often incorporate features to ensure compliance with industry regulations and standards, helping manufacturers adhere to legal requirements.
- Scalability and Flexibility: ERP software can be scaled up or down to accommodate the changing needs of the business. It is adaptable to accommodate growth, acquisitions, and changes in the industry.
- Cost Savings: By optimizing processes, minimizing inventory carrying costs, and reducing manual effort, ERP software can lead to cost savings in the long run.
The Role of ERP in the Manufacturing Industry
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software plays a crucial role in the manufacturing industry, offering a comprehensive solution that integrates various business processes and data into a single unified system. It streamlines operations, enhances productivity, and enables better decision-making across all levels of the manufacturing process. Here are the key aspects of ERP in the manufacturing industry:
a. Enhancing Production Planning and Scheduling
Production planning and scheduling are critical components of the manufacturing process. ERP software provides tools and functionalities that enable manufacturers to efficiently plan and schedule their production activities. With real-time access to data on inventory levels, customer demands, and resource availability, manufacturers can create accurate production schedules.
The software also helps allocate resources effectively, such as labor, machines, and materials, to optimize production efficiency and reduce downtime. It takes into account capacity constraints, such as machine capacities and worker availability, to ensure that production schedules are feasible and achievable.
b. Optimizing Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is essential for manufacturing companies to balance the cost of holding inventory against the risk of stockouts. ERP software with real-time data capabilities allows manufacturers to monitor inventory levels continuously. This visibility helps them maintain optimal inventory levels, reducing carrying costs associated with excess inventory and minimizing the risk of stockouts that can lead to production delays or dissatisfied customers.
By integrating inventory data with other business processes, such as production planning and sales, ERP systems facilitate a holistic view of inventory needs, ensuring the right products are available at the right time.
c. Improving Quality Control and Compliance
In the manufacturing industry, maintaining high-quality standards is crucial to ensure customer satisfaction and meet industry regulations. ERP systems assist in implementing robust quality control measures by enabling manufacturers to track and monitor various quality parameters throughout the production process.
ERP software can automate quality checks, capture data on product defects or non-conformances, and initiate corrective actions promptly. This helps ensure that products meet specified standards and comply with industry regulations and safety requirements.
d. Enhancing Supply Chain Management
The manufacturing industry relies heavily on a complex network of suppliers and vendors. ERP software streamlines supply chain management by providing visibility and control over the entire supply chain process.
Manufacturers can use ERP systems to coordinate and communicate with suppliers, facilitating efficient procurement processes. With real-time data on supplier performance, lead times, and costs, manufacturers can make informed decisions about their supply chain partners, ensuring reliability and cost-effectiveness.
Furthermore, ERP systems can assist in tracking the movement of materials and components throughout the supply chain, enabling manufacturers to respond quickly to any disruptions or delays.
Key Features of ERP Software for Manufacturing
a. Shop Floor Control and Machine Integration
One of the key features of ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software for manufacturing is its ability to provide shop floor control and machine integration. This feature allows manufacturers to closely monitor and manage their production processes in real-time. By integrating with machines and equipment on the shop floor, the ERP system can collect data directly from these devices, enabling seamless communication between different production stages.
With shop floor control, manufacturers can gain insights into the status of ongoing production activities, track work orders, and monitor the progress of various manufacturing tasks. This real-time visibility enables better decision-making, as supervisors and managers can identify bottlenecks, allocate resources more efficiently, and make adjustments to optimize production schedules.
The machine integration aspect of ERP software allows for automatic data capture from production machinery. This means that data such as production output, machine performance metrics, and downtime can be directly fed into the ERP system without manual intervention. This data integration streamlines the production reporting process and ensures accurate and up-to-date information on machine performance and utilization.
b. Material Requirement Planning (MRP)
Material Requirement Planning (MRP) is a critical functionality in ERP software designed for manufacturing companies. MRP modules within the ERP system help calculate the precise material requirements needed for the production process. By analyzing the production schedule, taking into account the bill of materials (BOM) for each product, and considering existing inventory levels, the MRP module ensures that the right materials are available at the right time for smooth production flow.
The MRP feature helps manufacturers avoid material shortages and production delays by generating purchase orders or production orders for required materials in a timely manner. It also considers lead times for material procurement and provides visibility into future material demands, enabling proactive planning and inventory management.
c. Work Order Management
Work order management is another crucial aspect of ERP software for manufacturing. This feature streamlines the process of creating, tracking, and managing work orders throughout the production lifecycle. A work order typically includes detailed instructions, specifications, and schedules for completing specific production tasks.
With work order management in ERP, manufacturers can efficiently allocate resources, track progress, and ensure that tasks are completed on time. This visibility into work progress enables better coordination among different teams involved in the production process. Additionally, it helps identify potential issues or delays early on, allowing for timely intervention and adjustments to meet production deadlines.
d. Batch and Lot Tracking
For industries that engage in batch or lot-based production, ERP systems offer batch and lot tracking capabilities. This feature ensures better traceability and accountability for products manufactured in batches or lots.
With batch and lot tracking, manufacturers can identify the origin of raw materials used in specific batches, track the production process for each batch, and trace the distribution and sales of finished products. This is particularly important in industries where product recalls or quality control issues may arise, as the ERP system can quickly identify affected batches and help with the recall process.
Implementing ERP Software in Manufacturing
a. Assessing Business Needs and Requirements
The first step in implementing ERP software in the manufacturing sector is to assess the specific needs and requirements of the business. This involves a thorough analysis of the existing processes and workflows within the manufacturing company. The key areas to focus on include inventory management, production planning, quality control, supply chain management, human resources, financial management, and customer relationship management.
During this assessment phase, the manufacturing company must also consider its budget constraints and the scalability requirements. ERP implementation is a significant investment, so understanding the financial capabilities and long-term growth plans is essential. Manufacturers should identify their current pain points and inefficiencies, as well as the goals they aim to achieve with the ERP system.
b. Choosing the Right ERP Solution
Once the business needs and requirements have been identified, the next crucial step is to select the appropriate ERP solution. Manufacturers should evaluate various ERP vendors and systems based on several factors. One critical consideration is the ERP system’s industry specialization. Some ERP software is tailored to meet the specific needs of manufacturing businesses, providing industry-specific functionalities and features.
Customization options are also crucial. Manufacturers often have unique processes and workflows that may require some level of customization to fit the ERP system effectively. Therefore, it is essential to choose a flexible ERP solution that allows for customization without compromising its core functionalities.
User-friendliness is another key factor to consider. The ERP system will be used by employees across different departments, and a user-friendly interface will ensure better adoption and utilization of the software.
c. Preparing for ERP Implementation
Before the actual implementation of the ERP system, manufacturers need to undertake comprehensive preparation. This includes:
- Data Cleansing: Ensuring that the existing data is accurate, consistent, and devoid of duplicates is crucial. Data cleansing helps prevent issues during data migration and ensures the ERP system starts with a clean and reliable dataset.
- Employee Training: Proper training is essential to familiarize the employees with the new ERP system and its functionalities. This ensures that the workforce is comfortable using the software and can leverage its capabilities effectively.
- Defining Implementation Goals and Timelines: Manufacturers should set clear goals for the ERP implementation process, such as specific improvements in efficiency, reduced lead times, or enhanced inventory management. Setting realistic timelines and milestones for the implementation project helps track progress and ensures timely completion.
d. Overcoming Implementation Challenges
ERP implementation in manufacturing can present various challenges that need to be addressed to ensure successful deployment. Some common challenges include:
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist the adoption of new processes and technologies. Overcoming this resistance requires effective change management strategies, communication, and involving employees in the decision-making process.
- Data Migration Issues: Migrating data from legacy systems to the new ERP can be complex and may lead to data integrity issues. Careful planning, testing, and validation of data are necessary to avoid disruptions.
- System Integration Complexities: Integrating the ERP system with existing software applications and machinery on the manufacturing floor can be challenging. Compatibility and seamless integration are crucial for smooth operations.
Cloud-Based ERP for Manufacturing: The Future of Industry
a. Understanding Cloud-Based ERP
Cloud-Based ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is a modern software solution that brings together various aspects of a manufacturing business into a unified and centralized system, hosted on the cloud. Unlike traditional ERP systems that are installed on-premises and managed by the company’s IT department, cloud-based ERP operates on a remote server maintained by a third-party provider. This means that the software and data are accessible through the internet, allowing users to access the ERP system from anywhere with an internet connection.
Cloud-based ERP offers several key advantages compared to on-premises solutions. One of the most significant benefits is scalability. Businesses can easily scale up or down their ERP resources based on their needs, without the need for significant hardware upgrades or investments. This flexibility makes it particularly appealing to manufacturing companies that may experience fluctuations in their operations.
Furthermore, cloud ERP solutions provide a high level of flexibility, as they can be accessed from various devices, including computers, tablets, and smartphones. This enables remote access, allowing employees to work from different locations, fostering collaboration and facilitating real-time decision-making.
Lastly, cloud-based ERP tends to be cost-effective compared to traditional ERP systems. With on-premises solutions, companies need to invest in expensive hardware, ongoing maintenance, and dedicated IT staff. In contrast, cloud ERP providers typically offer subscription-based pricing models, allowing businesses to pay for only the resources they use, without the burden of hardware maintenance.
b. Advantages of Cloud-Based ERP in Manufacturing
- Real-Time Data Access: Cloud ERP enables manufacturing businesses to access real-time data related to production, inventory, orders, and other critical aspects of their operations. This up-to-date information is invaluable for making informed decisions and reacting quickly to changes in demand or supply.
- Remote Collaboration: Manufacturers often have multiple locations or work with global suppliers, partners, or customers. Cloud-based ERP facilitates seamless collaboration between these entities, as they can all access the same system and work on shared data, no matter their physical location.
- Reduced IT Infrastructure Costs: Since the ERP system is hosted on the cloud, there is no need for manufacturers to invest in expensive on-site servers and IT infrastructure. This reduction in hardware costs can lead to significant savings for the business.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Cloud ERP streamlines manufacturing processes by automating tasks, optimizing workflows, and providing real-time insights. This efficiency improvement can lead to faster production cycles and better resource utilization.
- Easy Updates and Maintenance: Cloud ERP providers handle software updates and maintenance, ensuring that manufacturers always have access to the latest features and security patches without needing to manage these tasks internally.
c. Addressing Security and Data Privacy Concerns
One of the primary concerns businesses have when considering cloud-based solutions is the security of their data, especially in the manufacturing industry, where proprietary designs and sensitive production information are involved. Cloud ERP providers are well aware of these concerns and implement robust security measures to protect their clients’ data.
Security features in cloud-based ERP may include:
- Encryption: Data is encrypted both during transmission and storage, ensuring that even if intercepted, it remains unreadable to unauthorized parties.
- Access Controls: Role-based access controls restrict data access to authorized personnel only, minimizing the risk of data breaches.
- Data Backups: Regular data backups are performed to prevent data loss in case of unforeseen incidents.
- Monitoring and Auditing: Cloud ERP providers continuously monitor their systems for potential security threats and conduct regular audits to ensure compliance with security standards.
- Compliance Certifications: Reputable cloud ERP providers often obtain industry-specific certifications, such as ISO 27001, to demonstrate their commitment to data security and privacy.
ERP for Small and Medium-Sized Manufacturers
a. Tailored Solutions for SMEs
ERP vendors offer scaled-down and cost-effective solutions for small and medium-sized manufacturers.
b. Streamlining Operations and Enhancing Growth
ERP software empowers SMEs with enterprise-level capabilities, enabling them to compete with larger players.
The Future of ERP in the Manufacturing Industry
a. Tailored Solutions for SMEs
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are traditionally associated with large corporations due to their complexity and cost. However, ERP vendors now recognize the needs of small and medium-sized manufacturers (SMEs) and offer tailored solutions specifically designed to cater to their requirements. These scaled-down ERP systems are more affordable, easier to implement, and customized to address the unique challenges and processes of SMEs in the manufacturing industry.
By providing SMEs with access to ERP solutions, these businesses can streamline their operations, improve efficiency, and gain better control over their resources. The tailored solutions ensure that SMEs can take advantage of the benefits of ERP without overwhelming them with unnecessary complexities, making it a practical investment for their growth and success.
b. Streamlining Operations and Enhancing Growth
ERP software serves as a comprehensive platform that integrates various business processes and functions across the entire manufacturing organization. By implementing ERP, SMEs can streamline their operations, automate workflows, and optimize resource utilization. This results in increased productivity, reduced manual errors, and better coordination between different departments.
Additionally, ERP empowers SMEs with enterprise-level capabilities, which allows them to compete more effectively with larger players in the industry. The software enables SMEs to improve their supply chain management, track inventory in real-time, manage production schedules efficiently, and enhance customer relationship management. With access to accurate and up-to-date information, SMEs can make informed decisions and respond quickly to market changes, paving the way for their growth and competitiveness.
The Future of ERP in the Manufacturing Industry:
a. Integration with IoT and AI
As technology continues to advance, ERP systems are evolving to keep pace with these changes. One significant trend in the future of ERP for the manufacturing industry is the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies. IoT devices embedded in manufacturing equipment and products can generate vast amounts of data related to production, quality, and maintenance. By integrating IoT with ERP, manufacturers can leverage this data for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and improved visibility into the production process.
Furthermore, AI integration with ERP can enhance automation and decision-making. AI algorithms can analyze data from various sources, detect patterns, and make predictions, enabling manufacturers to optimize their operations, reduce downtime, and make strategic business decisions based on data-driven insights.
b. Predictive Analytics and Data-Driven Insights
Predictive analytics is a significant development in the future of ERP for the manufacturing industry. By using historical data and AI-powered algorithms, ERP systems can forecast demand, identify potential supply chain disruptions, and predict maintenance needs. This proactive approach empowers manufacturers to anticipate market trends, optimize inventory levels, and ensure smooth production processes.
Data-driven insights provided by ERP systems will become increasingly valuable for manufacturers, helping them make better-informed decisions that can positively impact their overall efficiency and profitability.
c. Mobility and Remote Access
In the future, ERP systems for manufacturing will prioritize seamless mobility and remote access. Manufacturers need to access critical information and collaborate in real-time, even when they are away from their physical office or factory floor. Mobile ERP applications and cloud-based solutions will become more prevalent, allowing users to access the ERP system from any device with an internet connection.
This enhanced mobility and remote access will foster better collaboration between teams, suppliers, and customers, leading to quicker response times and improved overall efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ERP software has become an indispensable tool for the modern manufacturing industry. From streamlining production processes and optimizing inventory management to enhancing quality control and ensuring compliance, ERP systems play a pivotal role in driving operational efficiency and business growth. Whether it’s a large-scale enterprise or a small and medium-sized manufacturer, implementing the right ERP software tailored to specific needs is crucial for success in today’s competitive market.
Feel free to share your thoughts and continue the discussion in the comments section, don’t forget to share the article with your friends or your favorite social media. Hope it is useful!













Leave a Reply
View Comments